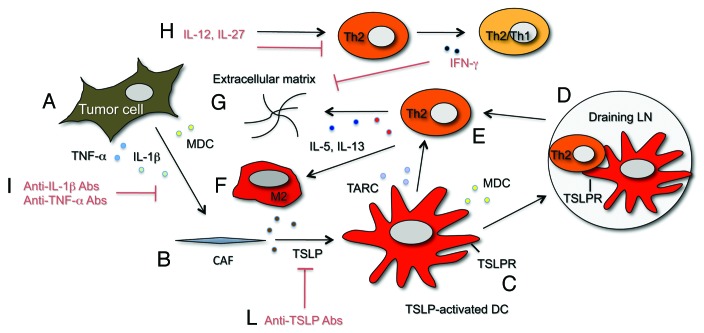
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of cytokine/chemokine and cell networks involved in and proposed therapeutic interventions to interfere with Th2 immune-deviation in pancreatic cancer. Tumor cells under the influence of yet unknown stimuli release pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNFα and IL-1β)(A) that induce TSLP release by CAFs (B). Resident DCs are activated/matured by TSLP, express the TSLPR (C) and migrate to draining LNs where they prime Th2 cells (D). Th2 cells are then recruited at the tumor site (E) by Th2 attracting chemokines (TARC and MDC) released by TSLP-activated DCs and tumor cells. Th2 cells release Th2 cytokines (IL-5 and IL-13) that further foster fibrosis by increasing extracellular matrix deposition (G) and possibly influence the development of M2 macrophages (F). In red are indicated potential therapeutic interventions to counteract at different levels the cytokine/chemokine network driving Th2 type inflammation. Anti-IL-1β and TNF-α Abs may be used to interfere with CAFs activation (I), anti-TSLP Abs to interfere with DCs conditioning (L). IL-27 and IL-12 were shown7 to inhibit Th2 cytokines and induce IFNγ production by Th2 cells (Th2/Th1 cells) (H). IFN-γ directly suppress collagen synthesis by fibroblasts6 (G). Cytokines/chemokines color code: IL-1β (light green), TNFα (light blue), IL-5 (dark blue), IL-13 (red), TSLP (brown), TARC (light violet), MDC (yellow).