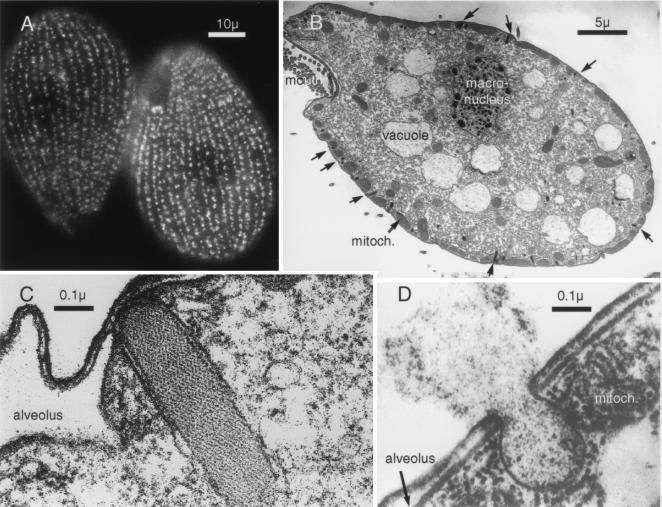
Figure 1.
Morphological features of Tetrahymena. (A) Immunofluorescence staining of mucocyst p80 demonstrates the presence of around 4,000 organelles arrayed as meridians covering the entire surface of the organism apart from the mouth structure. The cilia that provide locomotion lie between the meridians. (Scale bar = 10 μ.) (B) Electron micrograph of longitudinal section shows the mouth parts, digestive vacuoles and the macronucleus containing 45 copies of the five chromosomes. The mucocysts appear on the cell surface at docking sites interposed between mitochondria. (Scale bar = 5 μ.) (C) A docked mucocyst. The secretory material forms a compact paracrystalline core enveloped in a bilayer, which at the tip is apposed to the plasma membrane. On either side of the mucocyst are the flattened sacs of an alveolus, membrane-enveloped organelles that in ciliated protozoa act as dynamic Ca stores (30) (Scale bar = 0.1 μ.) (D) Exocytosis of a mucocyst shows fusion of the plasma and mucocyst membranes and expansion and expulsion of the mucocyst contents. The juxtaposition of the mitochondria and the mucocyst is also evident. (Scale bar = 0.1 μ.)