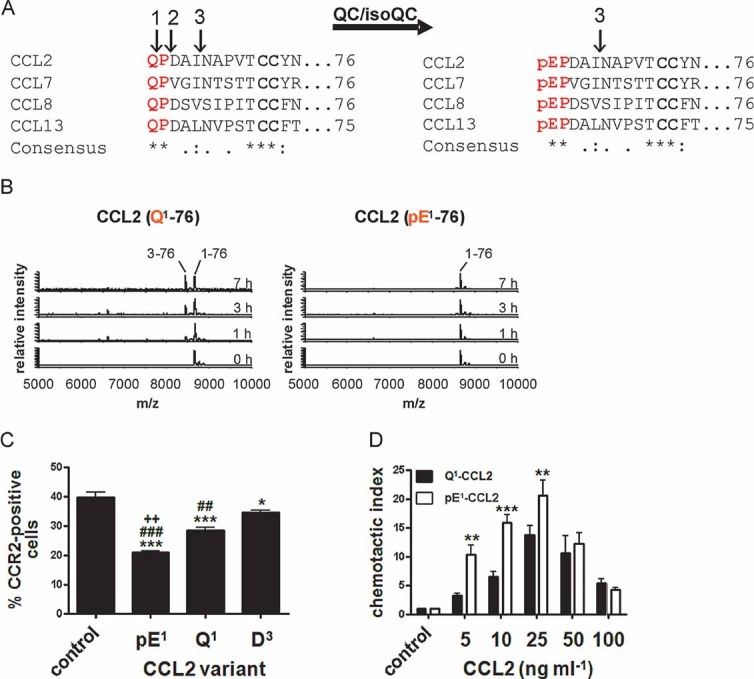
Immature forms of human MCPs, e.g. Q1-CCL2 display cleavage sites for ApP (1) and DP4 (2). CCL2 can also be processed by MMP-1 (3). All human MCPs are putative substrates of QC/isoQC and they contain in their mature state an N-terminal pE-residue and are protected against aminopeptidase cleavage but not against MMP-1 cleavage.
N-terminal degradation of human Q1-CCL2 and pE1-CCL2 in human plasma monitored using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
Internalization of CCR2 from the surface of THP-1 monocytes triggered by CCL2 variants and determined by FACS analysis. (***p < 0.001 and *p < 0.05 vs. control; ###p < 0.001 and ##p < 0.01 vs. D3, ++p < 0.01 vs. Q1, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test, n = 3–8, mean ± SEM).
Dependence of THP-1 monocyte migration on the concentration of CCL2(Q1-76) and CCL2(pE1-76), assessed using a chamber assay and quantification of cells by FACS analysis (***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, Q1-CCL2 vs. pE1-CCL2, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test, n = 3–7, mean ± SEM).