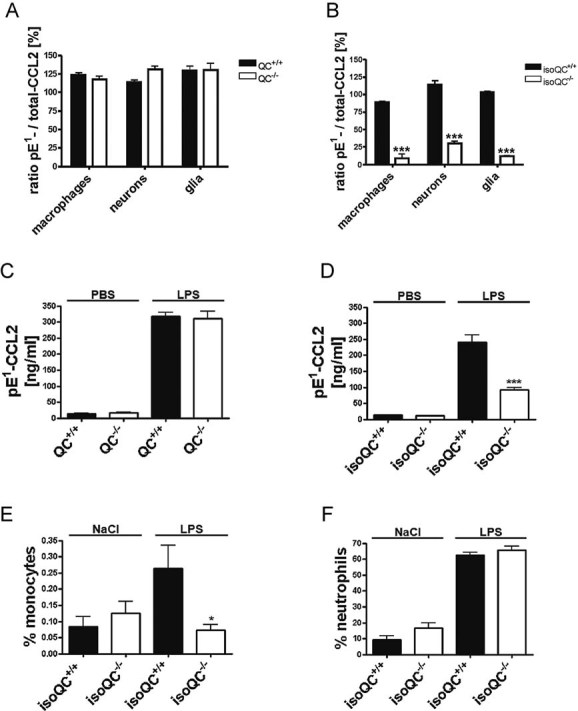
Analysis of the ratio of total-CCL2 and pE1-CCL2 secreted from LPS-stimulated primary cells isolated from QC−/− mice compared to WT littermates (QC+/+; n = 4–5, mean ± SEM).
Analysis of the ratio of total-CCL2 and pE1-CCL2 secreted from LPS-stimulated primary cells isolated from isoQC−/− mice compared to WT littermates (isoQC+/+; ***p < 0.001 vs. isoQC+/+, Student's t-test, n = 4, mean ± SEM).
pE1-CCL2 formation in serum after peripheral injection of LPS in male QC−/− mice compared to WT littermates (QC+/+; n = 6–7, mean ± SEM).
pE1-CCL2 formation in serum after peripheral injection of LPS in male isoQC−/− mice, compared to WT littermates (QC+/+; ***p < 0.001 vs. isoQC+/+ +LPS, Student's t-test, n = 5–8, mean ± SEM).
IsoQC-deficiency leads to impaired monocyte recruitment to lungs after intranasal LPS-application in isoQC−/− compared to WT littermates (isoQC+/+; *p < 0.05 vs. isoQC+/+ +LPS, Student's t-test, n = 7–8, mean ± SEM).
Analysis of neutrophils in bronchoalveolar fluid after intranasal LPS-application in isoQC−/− compared to WT littermates (isoQC+/+; n = 7–8, mean ± SEM).