Figure 2.
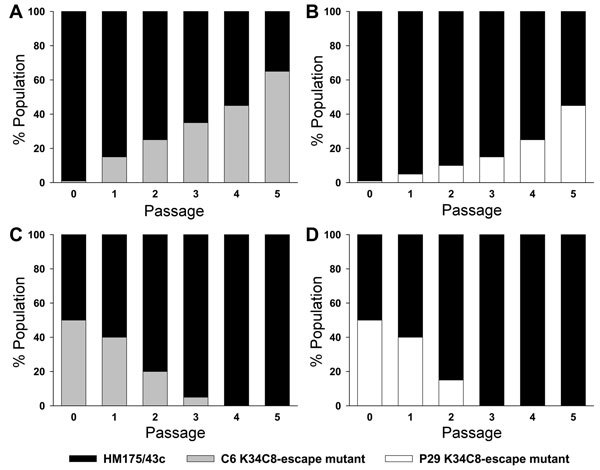
Growth competition experiments. Monoclonal antibody–resistant (MAR) mutants C6 (W1170C) and P29 (A1187P) were grown in competition with the HM175/43c (wild-type virus) in the presence (A, B) or in the absence (C, D) of the monoclonal antibody (MAb) K34C8. The MAR/wild-type ratios were 1:100 (104 50% tissue culture infective dose [TCID50] units of MAR mutants mixed with 106 TCID50 units of the wild-type virus in the presence of the K34C8 MAb) and 1:1 (106 TCID50 units of MAR mutants mixed with 106 TCID50 units of the wild-type virus in the absence of antibodies). In the competition experiments performed in the presence of antibodies, the initial viral mixtures as well as the viral progenies were neutralized with the MAb prior each infection passage. The proportion of mutant and wild-type phenotypes at each passage was inferred from the chromatogram of the consensus sequences and using as marker mutations W1170C and A1187P in C6 and P29 MARs, respectively (9).
