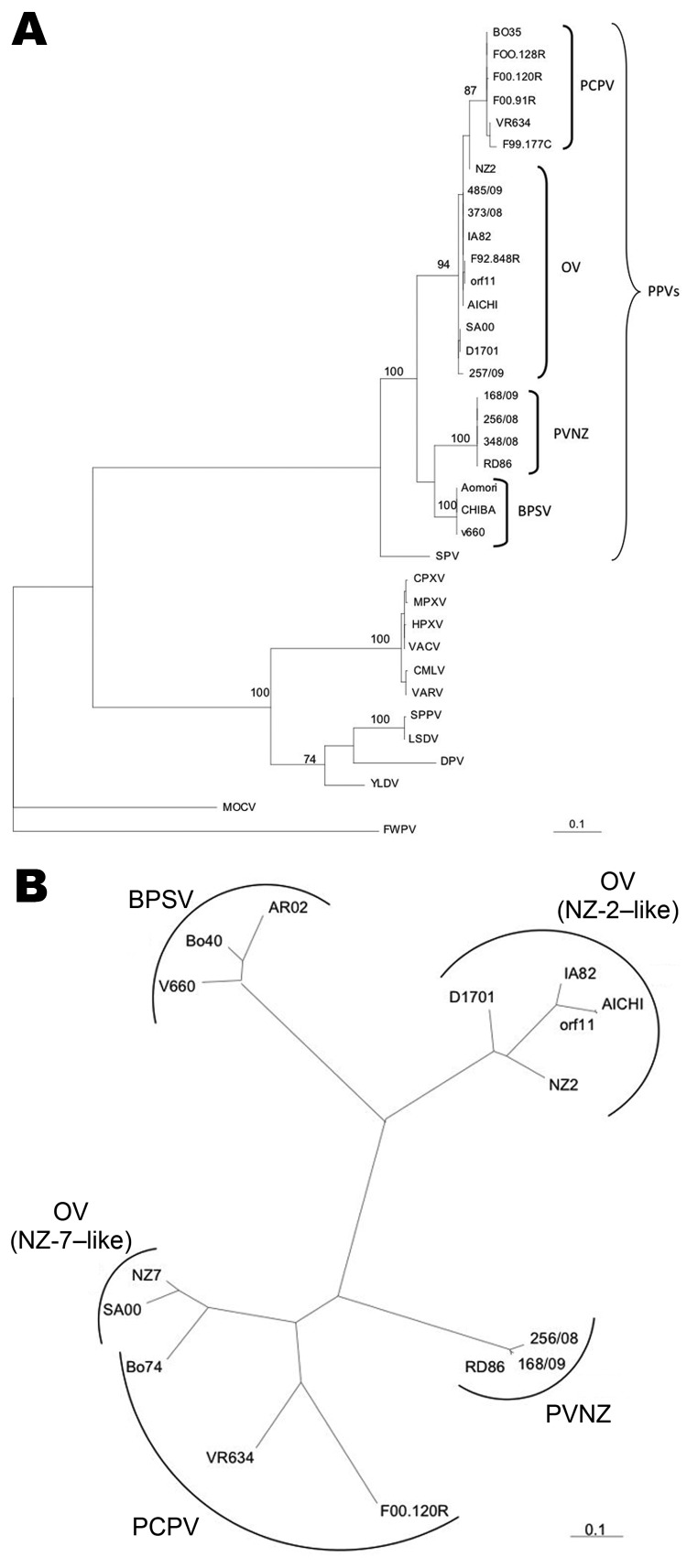
Figure 2.
A) Phylogenetic tree of chordopox virus (Table) calculated from the deduced amino acid sequences of the major envelop protein gene. Chordopox virus sequences were edited to correspond to the amino acid sequences of parapoxviruses and aligned by using ClustalW (www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw). Analyses were performed by using PHYLIP version 3.69 (distributed by J. Felsenstein, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA) and the maximum-likelihood method. Numbers on the nodes show the percentage of bootstrap calculated for 1,000 replicates. B) Phylogenetic tree based on the amino acid sequences of the parapoxviral vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene sequences. The genetic distance was estimated by using the Jones-Taylor-Thornton model of the program PRODIST and the phylogenies by using the Fitch-Margoliash method of FITCH (www.phylip.com). Tree was constructed by using PHYLIP version 3.69. Strain 348/08 is not shown because it shares 100% identity with RD-86. Scale bars indicate amino acid substitutions per site.