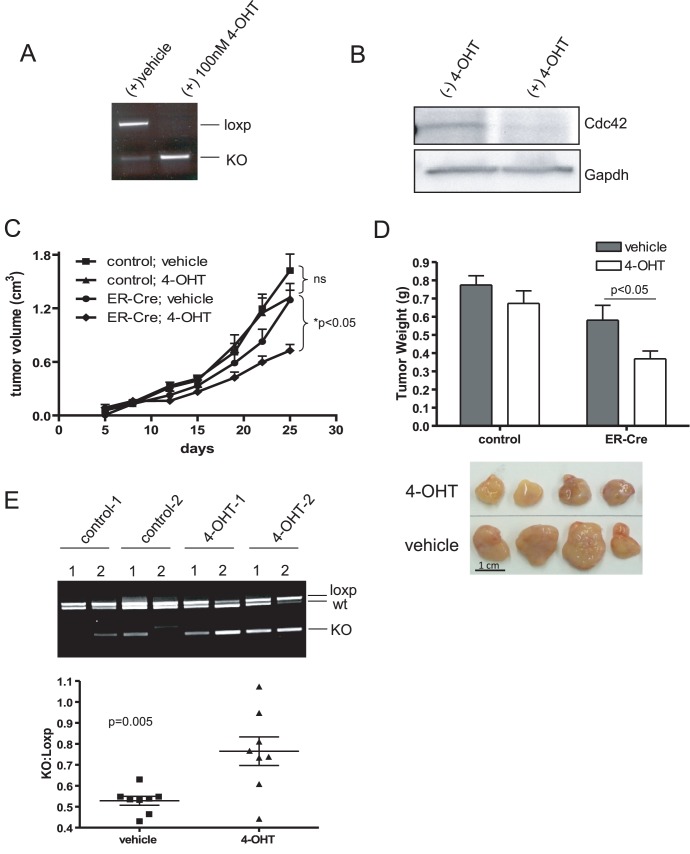
Figure 7. Cdc42 deletion in HRasV12-driven tumors inhibits tumor growth.
(a) HRasV12; Cdc42f/f cells were transduced with retroviral ER-Cre and selected with puromycin. Antibiotic resistant cells were pooled and treated in culture with 4-OH Tamoxifen (4-OHT) or vehicle. Recombination at the cdc42 locus was determined by PCR. (b) Cell lysates were isolated from cells cultured in the presence and absence of 4-OHT. Western blotting was performed to determine Cdc42 protein levels following Tamoxifen-induced recombination. (c) HRasV12; ER-Cre; Cdc42f/f and HRasV12; Cdc42f/f cells were injected into the flanks of immunocompromised nude mice. Five days post-injection, palpable tumors had formed and mice were administered 100 µl of 10 mg/ml 4-OHT in sunflower seed oil or vehicle control once a day, five days a week for 3 weeks. Tumor volume was monitored by caliper measurements. n = 8. (d) At 25 days post-injection, mice were sacrificed and tumors excised and weighed. A representative image of 4 HRasV12; ER-Cre; Cdc42f/f tumors treated with either tamoxifen or vehicle control is shown. (e) Genotyping was performed on DNA isolated from HRasV12; ER-Cre; Cdc42f/f tumors treated with either vehicle or 4-OHT to determine the status of the cdc42 locus. A representative image of genotyping results from two mice per condition (two tumors per mouse) is shown. Densitometry was performed using imageJ software and the intensity of the recombined cdc42 allele relative to the non-recombined cdc42 allele is plotted.