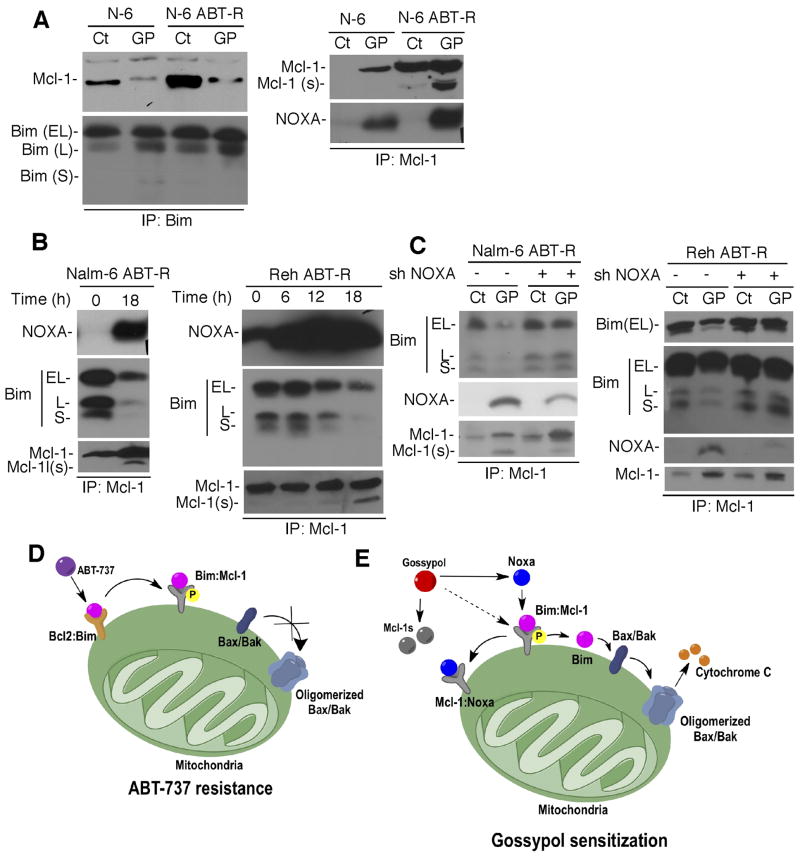
Figure 6. Interaction of NOXA with Mcl-1 triggers the release of Bim from Mcl-1 following gossypol treatment.
(A) Bim was immunoprecipitated from gossypol-treated cells followed by immunoblotting to determine Mcl-1 association (LHS). Immunoprecipitation for Mcl-1 was followed by immunoblotting for NOXA (RHS). (B) Association of NOXA and Bim with Mcl-1 were determined by immunoprecipitation-immunoblot analysis in gossypol-treated cells. (C) Mcl-1 immunoprecipitates from cells following NOXA knockdown and gossypol treatment were analyzed by immunoblotting for NOXA, Bim, and Mcl-1. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Model for ABT-737 resistance. ABT-737 does not target Mcl-1, which confers resistance by sequestering Bim displaced from Bcl-2. The Mcl-1/Bim association was enhanced by phosphorylation of Mcl-1, thereby preventing Bax activation. (E) Model for overcoming ABT-737 resistance by gossypol. Gossypol induces NOXA that binds to p-Mcl-1 and displaces Bim from the Mcl-1/Bim complex, leading to cell death that is augmented by Mcl-1s (splice variant) generation by gossypol treatment.