Figure 1. Generation of a hypomorphic Runx1 allele.
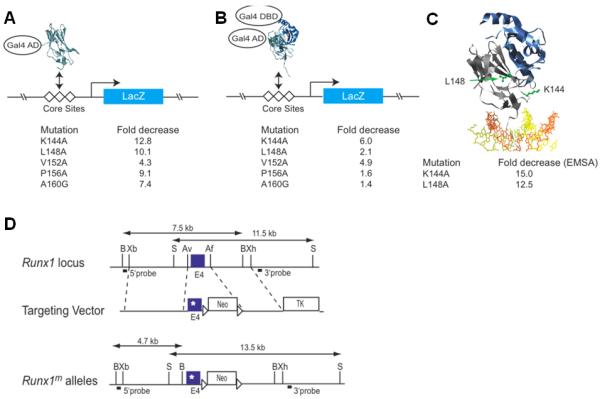
(A) Yeast one hybrid assay for Runt domain binding to three core sites driving lacZ expression. The Runt domain (RD) is fused to the GAL4 activation domain (GAL4 AD). Listed below are the relative decreases in β-galactosidase activity measured using a quantitative liquid assay. (B) Modified yeast one-hybrid assay to measure binding of the RD:CBFβ heterodimer to DNA. Although the Gal4 DNA-binding domain is fused to CBFβ in the modified yeast one-hybrid assay, there are no Gal4 binding sites on the promoter driving lacZ and therefore CBFβ’s activity is mediated only through the core sites. CBFβ increases the affinity of the RD for DNA by approximately 10-fold (44). (C) Ribbon diagram of the RD:CBFβ:DNA ternary complex (29,38) and the residues targeted for mutation. The Runt domain and CBFβ are shown in grey and blue, respectively, and DNA is orange and yellow. The side chains of K144 and L148 are shown and labeled in green. On the side are the fold decreases in DNA binding by purified Runt domain (in the absence of CBFβ) as determined by EMSA. (D) Targeting vector. Point mutations were engineered into exon 4 of Runx1. A neomycin resistance gene flanked by loxP sites is in intron 4. The location of probes and restriction length fragments from the wild type and targeted Runx1 alleles are indicated. B, BamHI; Xb, XbaI; S, SalI; Av, AvrII;, Af, AflII; Xh, XhoI.
