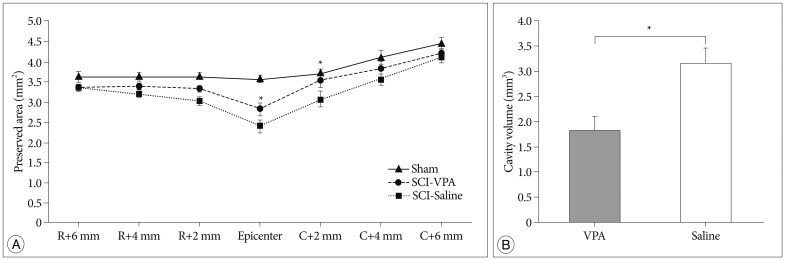
Fig. 3.
VPA improves spinal cord tissue sparing after SCI. A : Measurements of the average area of preserved cord tissues at the injury epicenter and adjacent sections at an interval of 2 mm up to 6 mm rostrally and caudally. B : Histogram showing the cavitation volume of the spinal cord lesion in both groups. There was a considerable reduction of the cavity volumes in the VPA-treated group compared to the saline-injected group. The error bars indicate SEM. *p<0.05 for VPA-injected groups vs. saline-injected groups after SCI. R : rostral, C : caudal (n=6/group), SCI : spinal cord injury, VPA : valproic acid, SEM : standard error of the mean.