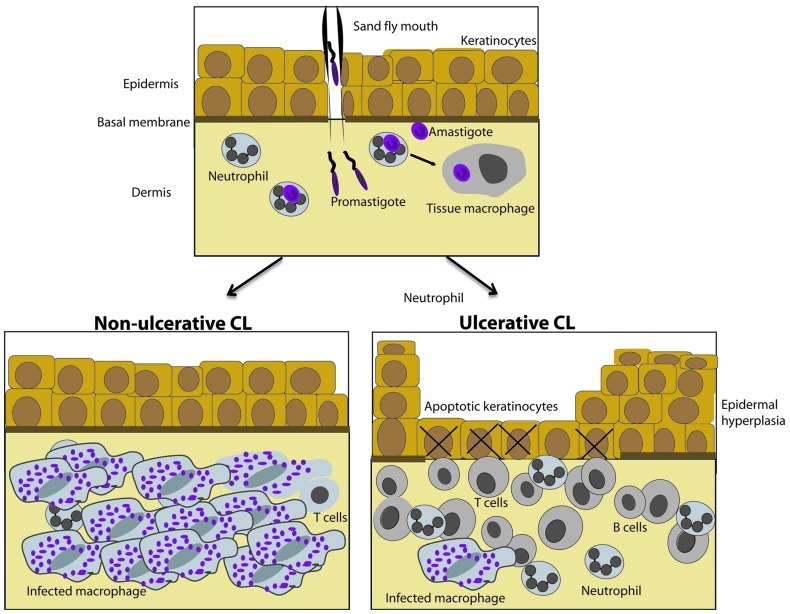
FIGURE 1.
Histological hallmarks of diffuse and localized cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by L. aethiopica. (Top) Neutrophils, dendritic cells, and tissue macrophages are targets for infective Leishmania promastigotes and are present in the healthy skin. (Bottom) L. aethiopica cause non-ulcerative diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis (DCL) or ulcerative localized cutaneous leishmaniasis (LCL). In non-ulcerative DCL (left), epidermis is intact and a large number of tissue macrophages packed with Leishmania amastigotes are present in dermis and the lymphocyte infiltrate is sparse as compared to ulcerative LCL (right). In ulcerative disease, apoptotic keratinocytes are present in the ulcerated epidermis. Epidermal hyperplasia and proliferating keratinocytes surround the ulcer and a dense inflammatory infiltrate is present in the dermal compartment. The number of infected tissue macrophages is low.