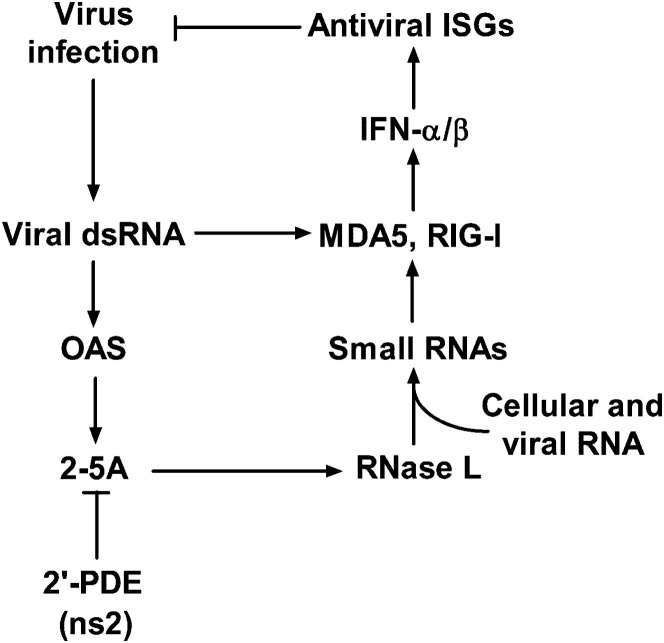
Figure 1.
The Interferon-Induced OAS-RNase L Pathway
After infection, viral RNA is detected by pattern recognition receptors RIG-I and MDA5, resulting in the induction of IFN-α/β, which in turn induces ISGs, including OAS. OAS is activated by dsRNA to produce 2-5A, which activates RNase L. RNase L degrades cellular and viral RNA producing more RNA that is recognized by MDA5 and RIG-I, resulting in enhanced IFN induction. 2′-PDE cleaves 2-5A and inhibits the activation of RNase L. MHV ns2, like the cellular enzyme 2′-PDE, is a 2′,5′-phosphodiesterase. OAS, 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase; 2-5A, 2′,5′ oligoadenylate; 2′-PDE, 2′-phosphodiesterase.