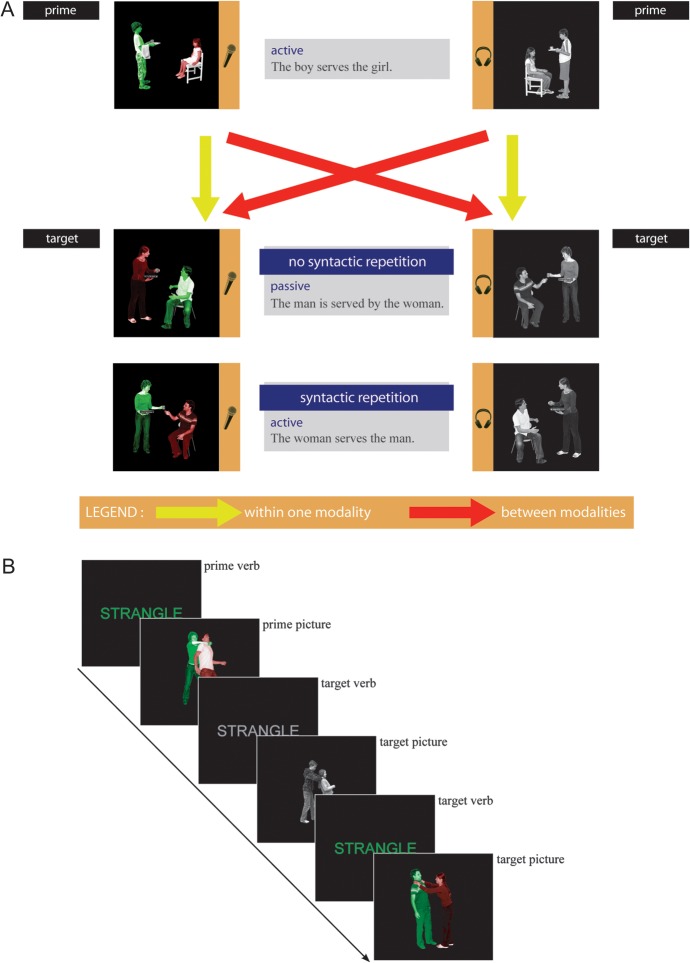
Figure 1.
(A) Design and stimuli. Participants either described colored photographs or listened to descriptions of grayscale photographs, containing action, agent, and patient. To guide production, participants were instructed to name the green actor before the red actor. Between subsequent sentences, that is, prime and target, the syntactic structure and the processing modality could be repeated (for syntax: active–active or passive–passive, for modality: production–production or comprehension–comprehension) or novel (for syntax: active–passive or passive–active, for modality: production–comprehension or comprehension–production). (B) Procedure. We used a running priming paradigm where each target item also served as a prime sentence for the next target item. The verb always preceded the photographs. Green verbs indicated a “production photograph” would follow, gray verbs indicated a “comprehension photograph” would follow.