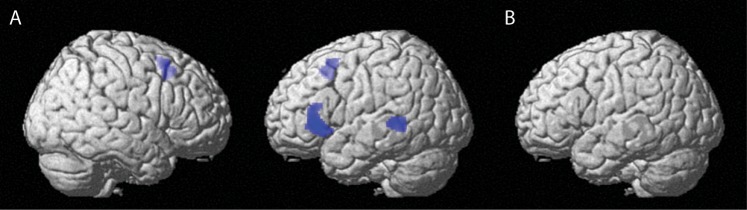
Figure 2.
Whole-brain results (see also Table 1). (A) The adaptation effects for syntax repetition. In left MTG, left IFG, and supplementary motor area, there was a repetition suppression effect for repeated compared with novel syntactic structures. (B) Interaction between syntax repetition and modality repetition. No regions showed an interaction between syntax repetition and modality repetition.