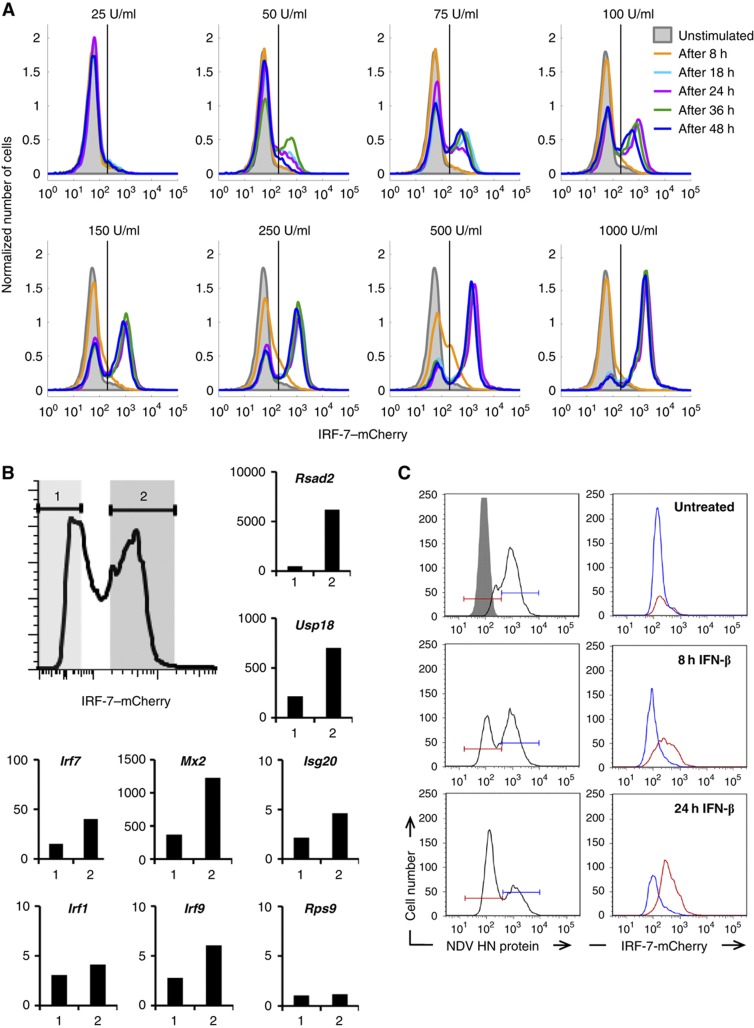
Figure 5.
Bimodal antiviral response towards IFN. A BAC-based reporter construct containing mCherry fused to the C-terminus of the chromosomal IRF-7 gene was integrated into NIH3T3 cells. Experiments were performed with a cell clone exhibiting a stable integration of the BAC and a representative response towards IFN. (A) Binary dose- and time-dependent IRF-7–mCherry expression. IRF-7–mCherry reporter cells were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of IFN-β, mCherry expression was determined by flow cytometry. (B, C) Bimodality of IRF-7 expression is reflected in ISG transcription and antiviral protection. (B) Reporter cells were treated with 500 U/ml IFN-β for 16 h and subjected to FACS. IRF-7–mCherry positive (2) and negative (1) populations indicated by the shaded areas were separated. RNA was prepared from both populations and analysed by qRT–PCR for expression of the indicated ISGs and Rps9 as a control. The results were normalized to β-actin mRNA and are shown as fold increase of untreated reporter cells. (C) Reporter cells treated with 500 U/ml IFN-β for 8 and 24 h were infected with 80 HAU/ml NDV. In all, 20 h after infection, cells positive (blue) or negative (red) for NDV HN (left column, intracellular antibody staining) were analysed for IFN-stimulated IRF-7–mCherry expression (right column) by flow cytometry.