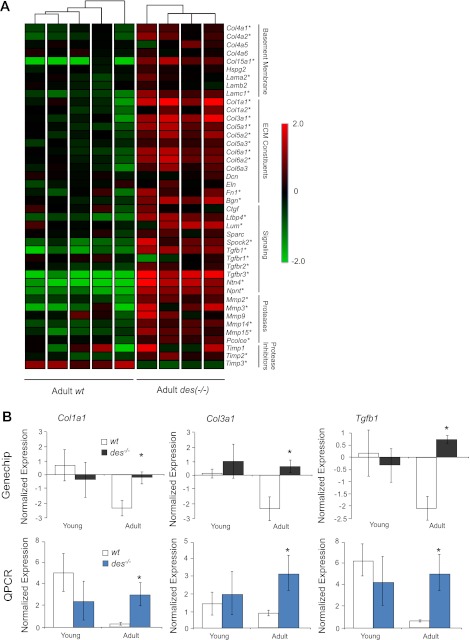
Fig. 3.
Adult des−/− muscle showed increased extracellular matrix (ECM) specific gene expression. A: normalized gene expression for 42 genes involved in ECM structure and maintenance is shown on a colored scale with green representing low expression and red representing high expression. Hierarchical clustering is represented by connecting lines at top of the grid with lines closest to the grid denoting the most similar samples. The clustering algorithm grouped samples according to genotype with adult des−/− in 1 group at right, indicating that adult des−/− samples had a distinct expression pattern of ECM genes compared with wt. Adult des−/− samples show higher expression of the majority of the listed genes indicated by their red color scheme. ECM-related genes are subdivided into 4 categories based on function: Basement Membrane, ECM Constituents, Proteases and Protease Inhibitors. *Significantly higher expression values, as determined by two-way ANOVA. B: normalized expression as determined by GeneChip and quantitative (q)PCR for 3 important ECM genes: Col1a1 (type I collagen), Col3a1 (type III collagen), and Tgfb1 (transforming growth factor-β). Consistent with GeneChip data, qPCR revealed significantly higher expression for all 3 genes in the adult des−/− muscle. *P < 0.05.