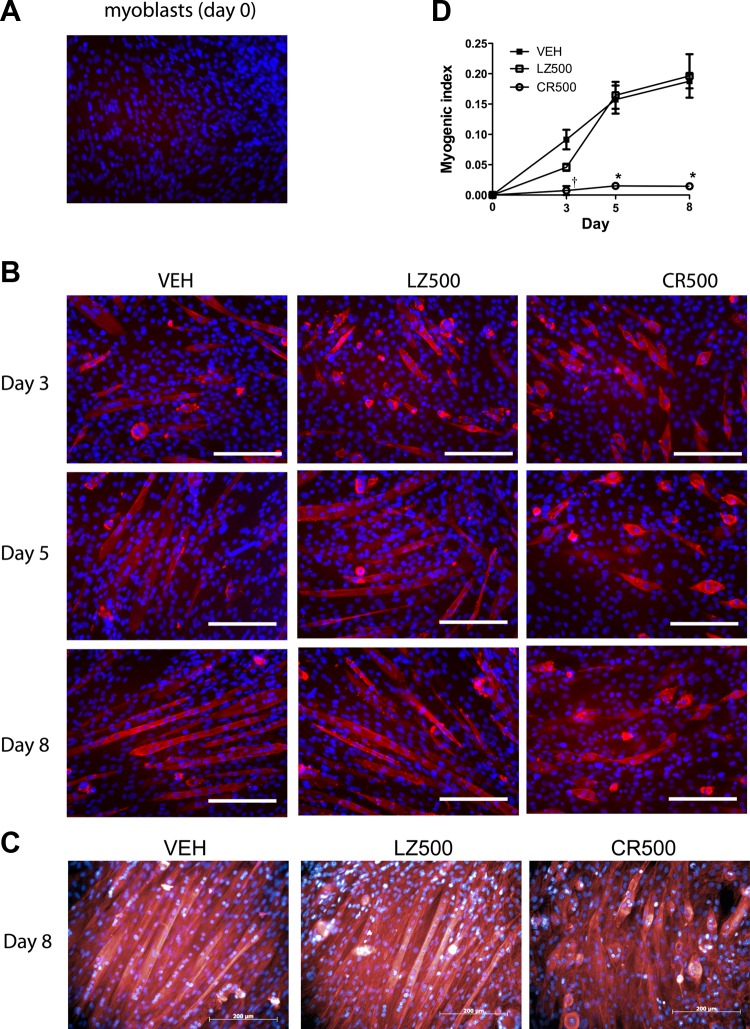
Fig. 3.
CMKLR1 knockdown impairs fusion of C2C12 myoblasts into myotubes. An anti-myosin heavy chain (MHC) antibody (red) was used to detect MHC protein in undifferentiated C2C12 myoblasts (A) and in differentiating C2C12 cells at the indicated differentiation time points following transduction with 500 multiplicity of infection of CMKRL1 shRNA (CR500)- and LZ-shRNA (LZ500) or vehicle (VEH) treatment (B). The cell nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). Each image is representative of 4 independent samples; scale bar = 200 μm. On day 8, F-actin filaments were stained with phalloidin (red) to visualize the formation of myotubes, and the cells were counterstained with Hoechst 33258 nuclear stain (blue) (C). Each image is representative of a total of 6 samples obtained from 2 independent experimental replicates; scale bar = 200 μm. The myogenic index was calculated as the ratio of nuclei in MHC-positive myotubes/total nuclei in the field of view (D). P < 0.05 compared with the VEH and LZ-shRNA controls at the indicated time point (*) and compared with the respective LZ-shRNA control only (†), two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni multiple-comparison test.