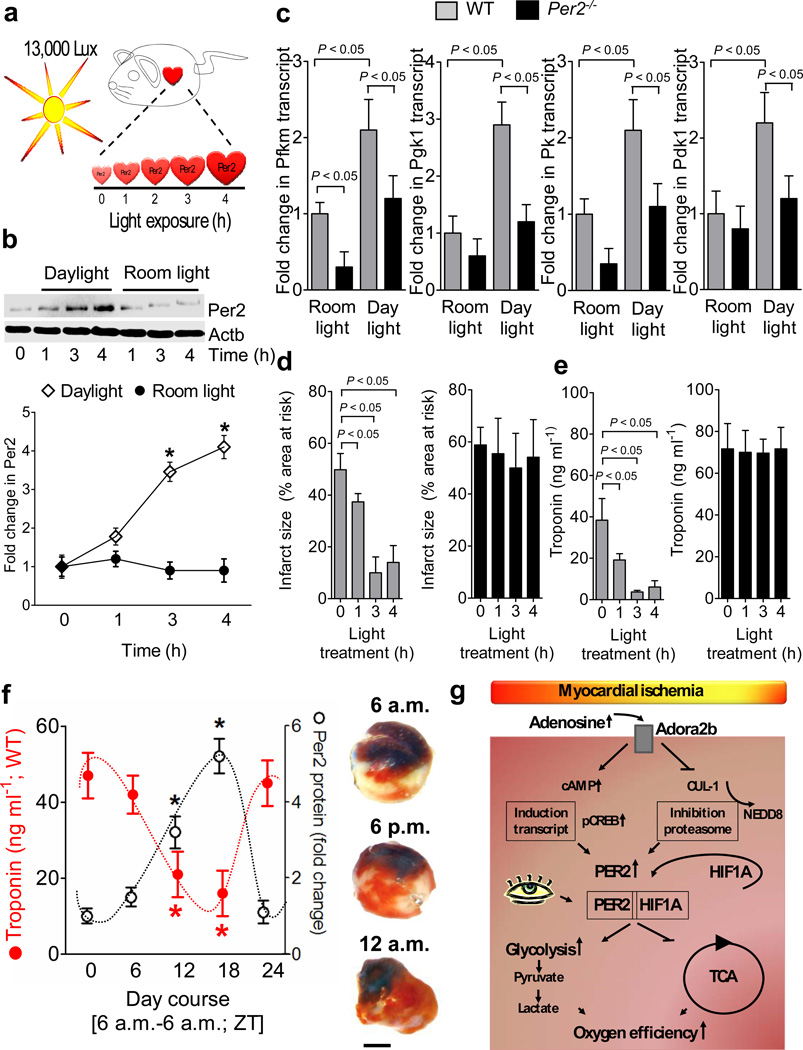
Figure 6. Light-induced stabilization of cardiac Per2 provides potent protection from myocardial ischemia.
(a) Experimental model for studying light-induced stabilization of cardiac Per2 levels. (b) Following exposure to 12h of darkness, mice were exposed to indicated times of intense daylight (13,000 lux) and compared to controls that were maintained at room light. Cardiac Per2 levels were analyzed by Western blotting (n=4 mice per group). (c) Alterations of transcript levels due to daylight exposure. Cardiac transcript levels of glycolytic key enzymes in Per2−/− mice or matched littermate controls after 4 hrs of light exposure (n=4 animals per condition; Pfkm: 6-phosphofructokinase-m; Pgk1: phosphoglycerate kinase 1; Pk: pyruvate kinase; Pdk1: pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isozyme 1). (g,e) Per2−/− mice or littermate controls matched in age, gender and weight underwent light therapy as described above over indicated time periods, followed by exposure to in situ myocardial ischemia (60 min) followed by 2h of reperfusion. Myocardial injury was assessed by measurement of Troponin I plasma levels (n=6 mice per experimental group) or infarct staining (see also Supplementary Fig S19b, n=6 animals per group, mean±SD). (f) Wild-type mice were subjected to in situ myocardial ischemia (60 min) followed by 2h of reperfusion over a 24 h time period. Troponin or infarct sizes (scale bar represents 50 µm) were correlated to Per2 protein levels using Per2 reporter mice (*p<0.05, n=8, mean±SD, Fig. 5a, Supplementary Fig. S19c). (g) Schematic model of Adora2b-dependent Per2 stabilization and its role in regulating anaerobic glycolysis and cardiac metabolism during myocardial ischemia.