Figure 5. ADEP-activated ClpP degrades nascent polypeptides in vitro.
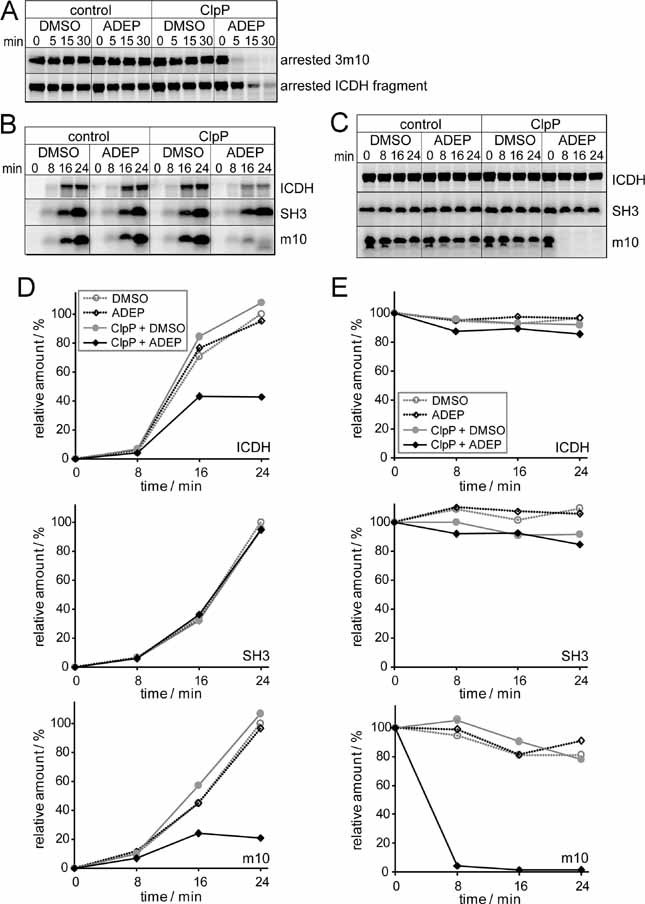
[35S] methionine-labelled model polypeptides (a ribosome-arrested ICDH fragment of 45 kDa, a ribosome-arrested 3m10-SecM chain of 26 kDa (A) and non-arrested full-length ICDH (46 kDa), SH3 and m10 (B and C) were synthesized in an E. coli-based transcription/translation system and analysed for degradation at 37 °C. Polypeptides were separated on tricine gels and visualized by autoradiography. Only the full-length products are depicted.
A. ClpP, ADEP and DMSO were added to the translation system after the generation of ribosome-arrested nascent chains.
B. ClpP, ADEP and DMSO were added to the translation system before the synthesis of full-length, non-arrested polypeptides.
C. ClpP, ADEP and DMSO added after the translation of full-length, released polypeptides.
D, E. Quantification of the degradation experiments shown in (B) and (C), respectively. The amount of full-length product at the end of translation under control conditions (DMSO without ClpP addition) was set at 100%. The data correspond to one representative experiment out of three and a second experiment, performed using another purification of the translation extract, is depicted in the Supporting Information Fig 1.
