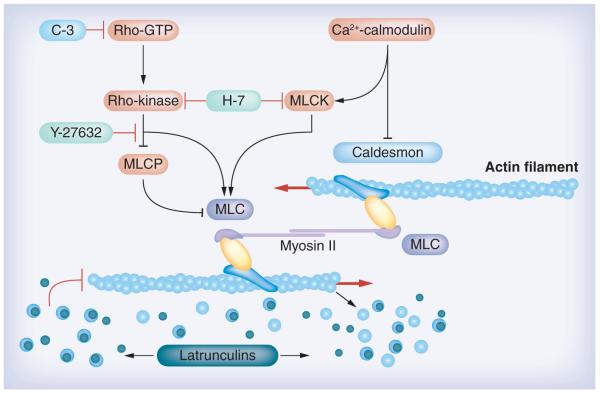
Figure 1. Targets where agents (or proteins) can disrupt the actin cytoskeleton and enhance outflow facility.
Rho kinase inhibitors, including the nonselective Rho kinase inhibitor H-7 and the specific Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (and other specific Rho kinase inhibitors as indicated in the article), block the Rho cascade, inhibiting actomyosin contraction and disrupting actin stress fibers. H-7 also blocks MLCK, which may affect myosin light-chain phosphorylation and, in turn, interfere with actin–myosin interactions. Actin filament disruptors latrunculins (e.g., latrunculins A and B) sequester monomeric G-actin leading to microfilament disassembly. The cytoskeleton-modulating proteins caldesmon and C3 affect the actin cytoskeleton similar to the compounds as indicated above. Caldesmon negatively regulates actin–myosin interactions, and C3 blocks the Rho cascade similar to Rho kinase inhibitors.
Modified with permission from a figure in [87] © Elsevier. The figure was originally created by Alexander Bershadsky.