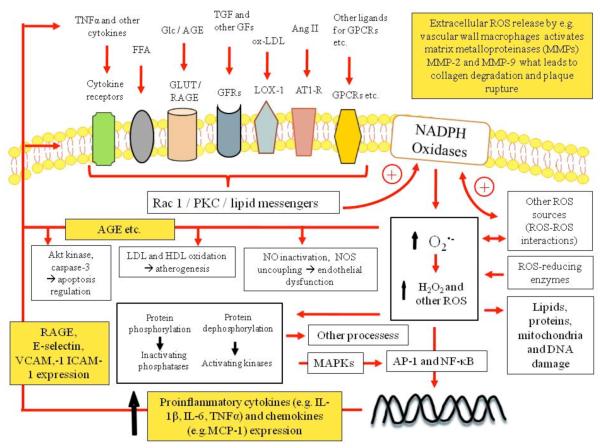
Figure 2. NADPH oxidase regulation and intracellular ROS signaling pathways.
Activation of growth factor receptors (GFR), lectin-like ox-LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1), angiotensin type 1-receptor (AT1-R) and other G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), various cytokines and other receptors lead to Rac1 and/or protein kinase C (PKC) activation and/or lipid messenger production, which induces NADPH oxidase. Superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide change intracellular protein phosphorylation, regulate redox sensitive gene expression, induce damage, mediate cell survival, growth, proliferation, migration and numerous other processes. MAPKs – mitogen-activated protein kinases ; AP-1 - activator protein-1; NF-κB - Nuclear factor-κB; (R)AGE – (receptor of) advanced glycation end-products; VCAM-1 - vascular cell adhesion molecule – 1; ICAM-1 - intercellular adhesion molecule – 1; MCP-1 – monocyte chemoattractant protein –1.