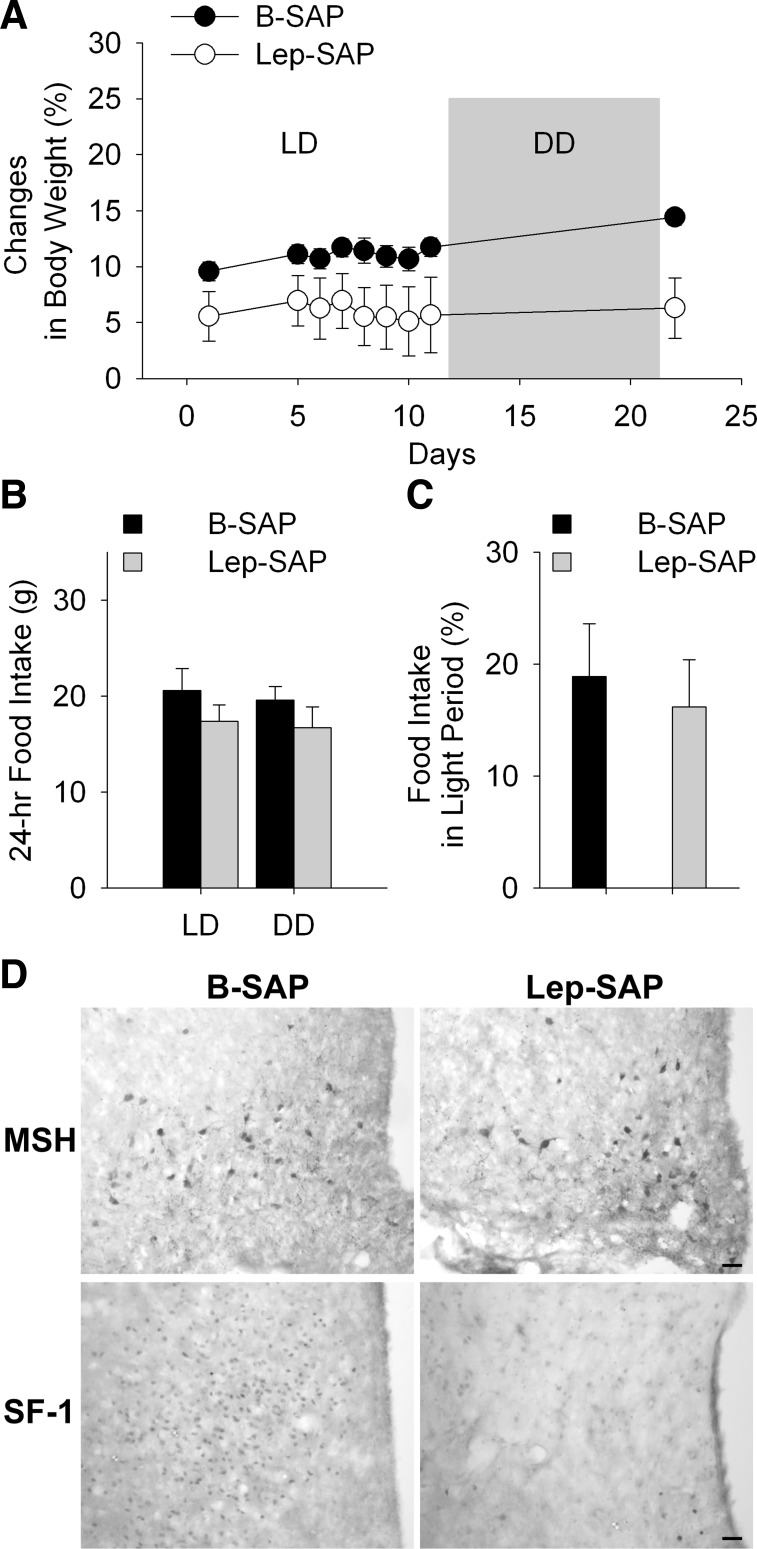
Fig. 7.
Body weight and food intake and hypothalamic IHC in rats injected into the ventromedial nuclei of the hypothalamus (VMN) with B-SAP or Lep-SAP. A–C: body weight and food intake in VMN Lep-SAP and B-SAP rats. Body weight gain (A), shown as a percentage of body weight at the time of VMN injections. There was no difference in body weight between B-SAP (n = 6) and Lep-SAP (n = 7) rats at the time of surgery. Body weights and feeding are shown for two testing conditions, LD and DD (gray box in A), beginning 7 wk after the VMN injections. Lep-SAP rats weigh significantly less than B-SAPs across all test days (P < 0.05). Twenty-four-hour food intake (B) and percent of food intake during light period over daily intake (C) did not differ significantly between VMN B-SAP and Lep-SAP rats in LD. D: coronal sections of rat brain showing Arc and VMN in VMN B-SAP or Lep-SAP rats. The Arc sections were immunoreacted to reveal α-MSH cell bodies (top), which are localized to the Arc. The VMN sections were immunoreacted to reveal nuclei positive for SF-1, a peptide located within the VMN (bottom). Calibration bar = 20 μm.