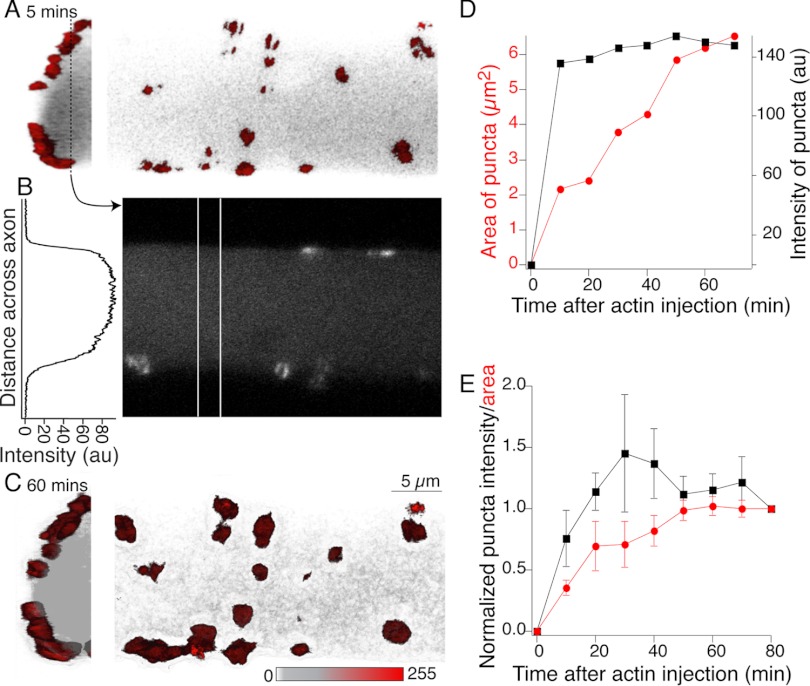
Fig. 2.
G-actin incorporates into presynaptic puncta but not cortical actin. Reticulospinal axon impaled with a microelectrode containing Alexa Fluor 488 G-actin (1.1 mg/ml) and buffer solution (2 mM HEPES, 0.2 mM CaCl2, 0.2 mM ATP, pH 8.0). This was pressure injected into the axon. Fluorescent actin structures formed within minutes of injection and increased in fluorescence over 80 min. A: 3D reconstruction of actin fluorescence close to the axon perimeter 5 min after injection. Hemi-axon is shown in transverse section (left) and from the ventral spinal surface (right). Red structures are bright actin labeling consistent with synaptic vesicle cluster colocalization; gray is the diffuse labeled G-actin within the axon. B: single optical section shown in linear grayscale taken from the dashed line in A. The graph is a profile plot of intensity taken from between the vertical white lines. There is no cortical actin signal. C: same views as A but after an hour of recording. D: mean intensity (black) and cross-sectional area (red) of all clusters in A plotted with time after injection. E: mean area and intensity (6 preparations) normalized to value 80 min after injection.