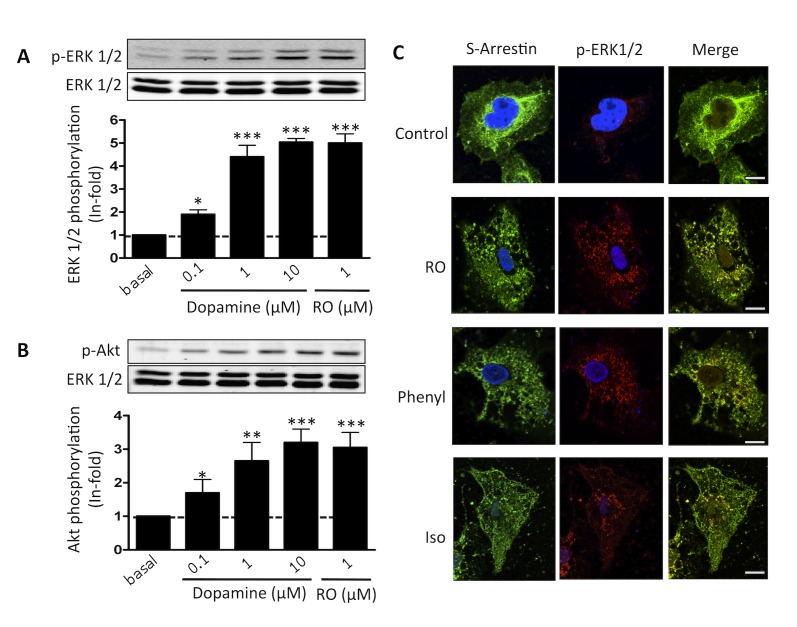
Figure 1. Functionality of dopamine D4 receptors in pineal gland and pinealocytes.
Pineal glands extracted at 9:00 h were treated for 10 min with increasing amounts of dopamine or with 1 µM of RO 10-5824 (RO). The immunoreactive bands, corresponding to ERK 1/2 (Thr183-Tyr185) phosphorylation (A) and Akt (Ser473) phosphorylation (B), of two separate experiments performed in duplicate were quantified and values represent the mean ± S.D. of the fold increase relative to basal levels found in untreated cells. Significant differences with respect to basal levels were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by a Dunnett's multiple comparison post hoc test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001). A representative Western blot is shown at the top (see Materials and Methods). (C) Pinealocytes were isolated from pineal glands extracted at 9:00 h and were treated with medium (Control), 1 µM of RO 10-5824 (RO), 1 µM phenylephrine (Phenyl), or 1 µM isoproterenol (Iso) for 10 min before labeling with anti-S-arrestin (green) and anti-phospho-ERK1/2 (red), as indicated in Materials and Methods. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 5 µm.