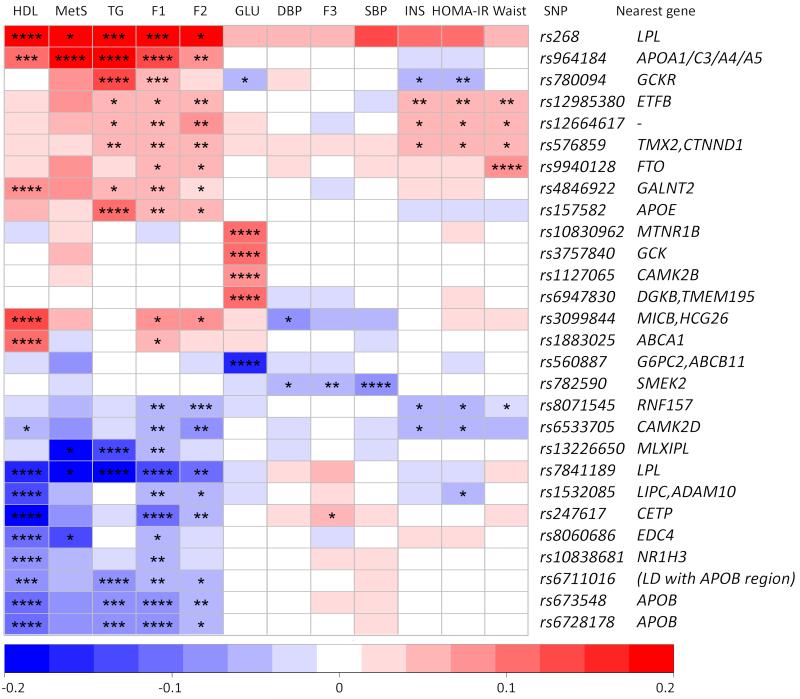
Figure 2.
SNP associations across MetS phenotypes. The plot shows SNP-phenotype associations for the twenty-two top hit SNPs from the MetS component GWA analysis (Figure S6 and Table S3), four top hit SNPs from the TG/HDL/waist circumference –factor analysis, and five SNPs with a suggestive association in the TG/HDL/waist circumference/HOMA-IR –factor analysis (overlapping SNPs excluded). The colours correspond to beta effect size values for the minor allele of the SNP (values above 0.2 have been recoded to 0.2 and values below −0.2 to −0.2 and positive values refer to a risk effect and negative values to a protective effect). Psig-values for the tests are shown as: * P < 0.01, ** P < 1×10−4, *** P < 1×10−6, **** P < 5×10−8. HDL, high-density lipoprotein; MetS, metabolic syndrome case-control status; TG, triglycerides; F1, TG/HDL/waist circumference -factor; F2, TG/HDL/waist circumference/HOMA-IR -factor; GLU, glucose; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; F3, SBP/DBP blood pressure factor; SBP, systolic blood pressure; INS, insulin; HOMA_IR, Homeostatic Model Assessment Insulin Resistance.