Figure 5.
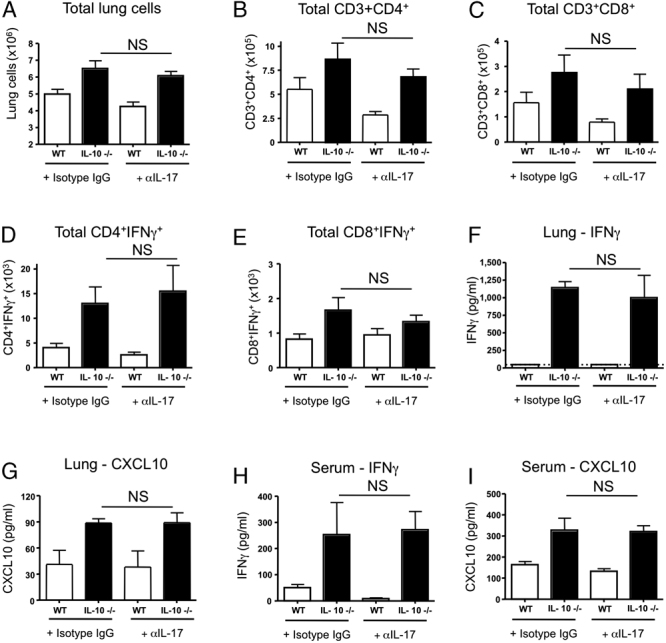
The enhanced cellular influx and IFN-γ production seen in IL-10−/− mice during Mtb infection are not IL-17 dependent. WT (open bars) and IL-10−/− (closed bars) BALB/c mice were infected with Mtb and treated twice weekly with either anti-IL-17 mAb or isotype IgG. Mice were killed on day 32 postinfection and the lungs isolated. (A) Total lung cell counts, (B) total CD4+ T cells and (C) total CD8+ T cells following IL-17 neutralization were determined by flow cytometry staining for CD3, CD4 and CD8. Whole lung homogenates from anti-IL-17-treated and isotype control-treated mice were restimulated with PPD and the total number of (D) CD4+IFN-γ+ and (E) CD8+IFN-γ+ cells in the lungs of infected WT and IL-10−/− BALBc mice was determined by flow cytometric analysis. Cell culture supernatants of the restimulated lung homogenates were analysed for (F) IFN-γ and (G) CXCL10. Serum levels of (H) IFN-γ and (I) CXCL10 from Mtb-infected Ab-treated mice were assayed as described in Fig. 4. Results (mean±SEM) shown are combined data from two independent experiments, totalling ten mice per group (A–E) or three to six mice per group (F–I). NS, nonsignificant (unpaired Student's t-test).
