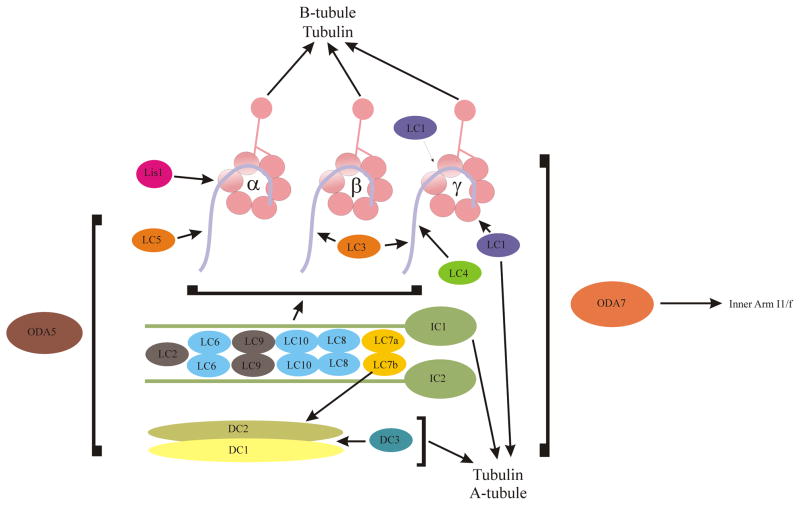
Figure 1. Composition and Organization of Outer Arm Dynein.
The composition and organization of the Chlamydomonas outer dynein arm is diagramed. This complex enzyme is built around three AAA+ motors (α, β, and γ) which associate directly with a series of LCs (LCs 1, 3, 4, 5) that transduce mechanical, Ca2+ and redox signals. The HCs in turn associate with a complex consisting of two WD-repeat ICs which contain N-terminal regions to which a series of LCs (LCs2, 6, 7a, 7b, 8 and 10) bind. One of these LCs (LC7a) interacts with a component of the trimeric docking complex that anchors the structure within the axoneme. The ODA5 protein is also required for assembly but its associations are uncertain (Wirschell et al., 2004). Finally, the ODA7 protein may mediate association of the outer arm with inner arm I1/f (Freshour et al., 2007).