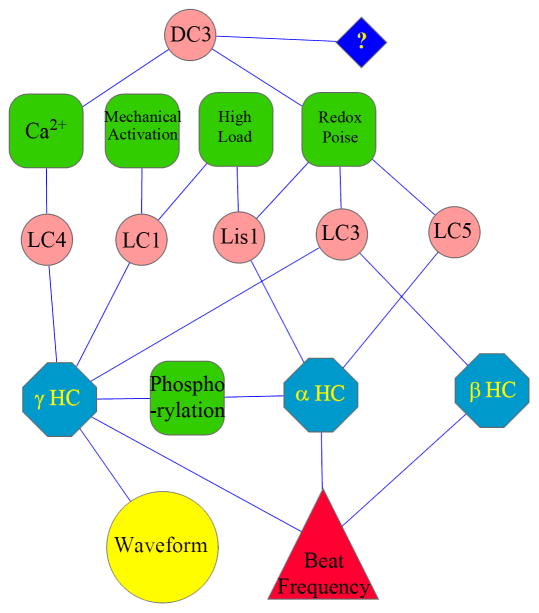
Figure 2. Integrated Signaling Pathway for Outer Arm Dynein.
This diagram illustrates the known signals that impinge on Chlamydomonas outer arm dynein (green), the effector molecules (pink), the distinct HC motor components (light blue) and the functional output (yellow/red). Of note is that each HC acts to integrate a distinct set of signals: redox, Lis1 and phosphorylation (α HC), redox (β HC), and Ca2+, mechanical sensing, phosphorylation, and redox state (γ HC). The lack of individual motor units also leads to distinct phenotypic results which likely derive from both alterations in motor function and disruption of particular signaling modalities.