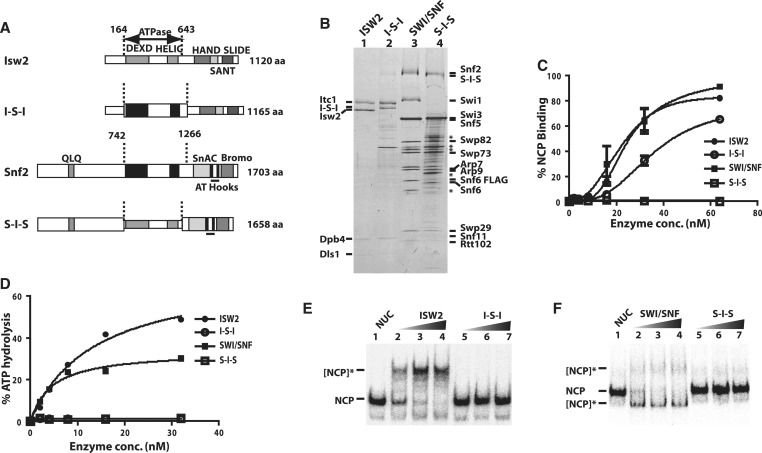
Figure 1.
The ATPase domains of SWI/SNF and ISW2 are not interchangeable. (A) The domain organization of Isw2 and Snf2 are shown along with the boundaries of the ATPase domains as dashed lines. The ATPase domains of Isw2 (gray) and Snf2 (black) are swapped with each other to make two hybrid catalytic subunits referred to as I-S-I and S-I-S. (B) The I-S-I and S-I-S subunits were purified along with their associated subunits and analyzed by 4–20% SDS–PAGE and Coomassie staining. The different subunits from SWI/SNF and ISW2 are indicated on either side. SWI/SNF had Snf6 tagged with two copies of FLAG epitope at its C-terminus instead of Snf2 being FLAG tagged as for the S-I-S. The asterisk indicates those protein bands which are not part of SWI/SNF, but co-purify with SWI/SNF when using M2 agarose. (C) The affinity of SWI/SNF and ISW2 for nucleosomes was compared to that of I-S-I and S-I-S by gel shift. Increasing amounts of enzyme were bound to 8 nM of end positioned 0N70 nucleosome. Error bars represent mean and standard deviation of two independent binding experiments. (D) The ATPase activity of SWI/SNF, ISW2, I-S-I and S-I-S with 0N70 nucleosomes was measured using γ-32P ATP and plotted. (E and F) The nucleosome remodeling activity of ISW2, I-S-I, SWI/SNF and S-I-S was measured by gel shift as shown with 0N70 nucleosomes (80 nM based on histone octamer). The concentrations of remodeler were 3, 10 and 15 nM. The reactions were incubated for 30 min at 30°C before stopping with competitor salmon sperm DNA and γ-S-ATP, and analyzed on 5% native polyacrylamide gel. NCP is nucleosome core particle and shows where nucleosomes migrated before remodeling. The [NCP]* indicates the position of the nucleosomes after being remodeled either by SWI/SNF or ISW2.