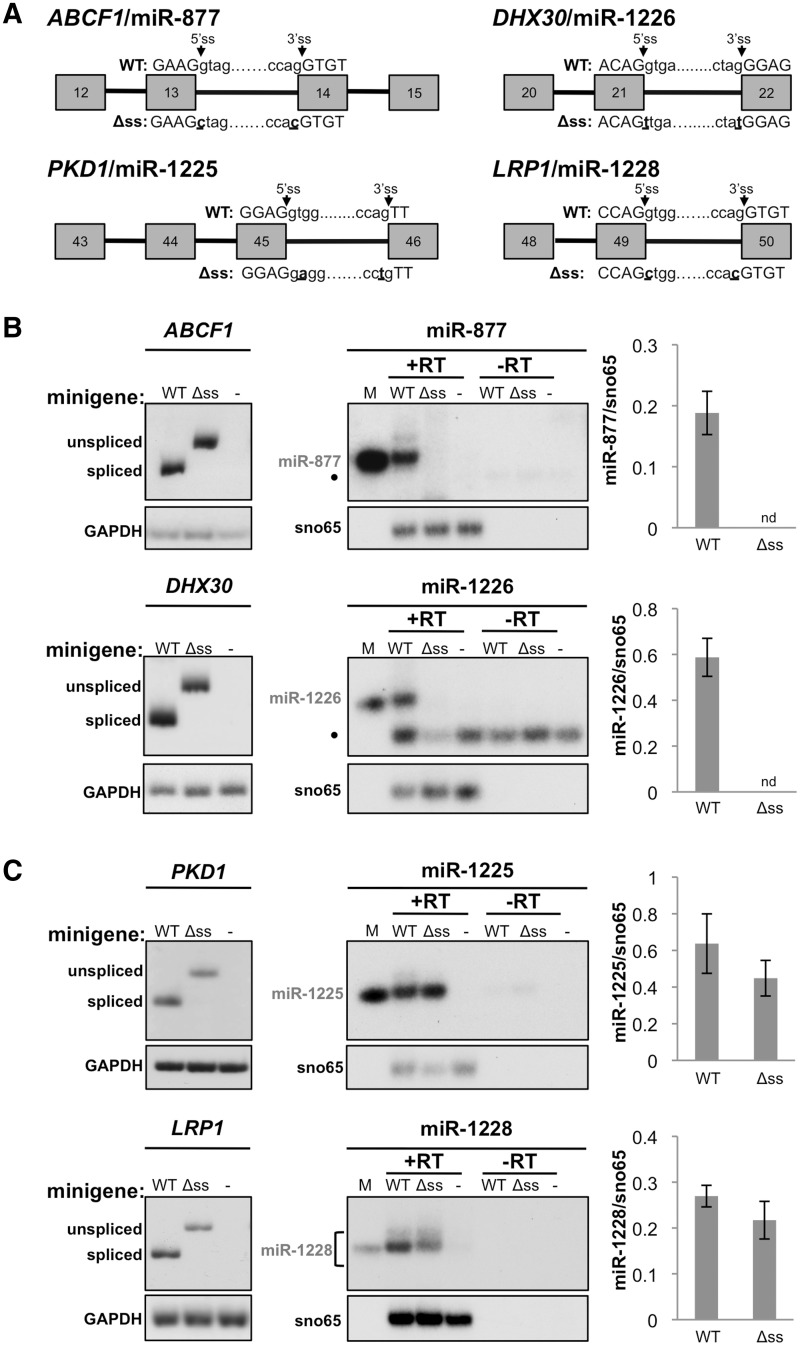
Figure 1.
Identification of splicing-independent mirtron-like miRNAs (simtrons). (A) Minigene structures. Boxes and lines indicate exons and introns, respectively. Splice site mutations are in bold and underlined. Arrows refer to the 5′ and 3′ splice sites (ss). (B) Splicing-dependent mirtrons. Left panels: splicing analysis of host gene transcripts. wt, splicing-deficient (Δss) minigene transcripts or empty vector control (−) were transfected into HEK-293T cells and mRNA splicing was analysed by radiolabelled RT–PCR. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Unspliced indicates the mRNA product retaining only the mirtronic intron, all other introns were excised. Middle panels: miRNA expression in minigene-transfected HEK-293T cells was analysed by radiolabelled, stemloop RT–PCR with snoRNA65 (sno65) used as a loading control. +RT indicates RNA that was reverse transcribed with stemloop primers and −RT indicates RNA that was not reverse transcribed but had stemloop primers added as a control. M indicates a synthetic size marker. Filled circle indicates a non-specific primer dimer. Right panels: Quantitation of miRNA expression normalized to sno65. nd indicates that the miRNA was not detected. Bars represent the average values ± SEM; ABCF1/miR-877 n = 12, DHX30/miR-1226 n = 11. (C) Splicing-independent mirtron-like miRNAs analysed as in B. PKD1/miR-1225, n = 8; LRP1/miR-1228, n = 9.