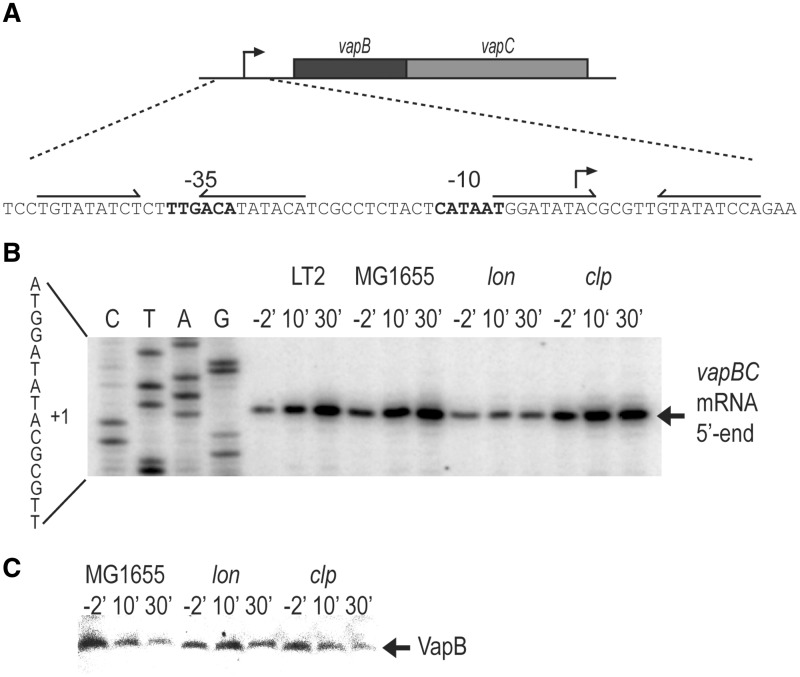
Figure 1.
Lon degrades VapB and is required for activation of vapBC transcription. (A) DNA sequence of the vapBC promoter region showing −10 and −35 promoter sequences and the two operators vapO1 and vapO2 as inverted repeats. (B) Primer extension analysis of the 5′-end of vapBC mRNA. Strains MG1655 (E. coli K-12, wt), KW10 (MG1655Δlon) or KW11 (MG1655ΔclpP) containing pKW71512 (pNDM71::vapBC) and KP1001 (S. enterica LT2) were grown exponentially in LB medium. At time zero, chloramphenicol (50 µg/ml) was added and cell samples were withdrawn at the time points indicated (min). Total RNA was extracted and reverse transcription was performed using primer vapB-5#PE. (C) Western blotting analysis of VapB. MG1655 KW10 or KW11 containing pKW51 (pA1/03/04::SDopt::vapB) were grown exponentially in LB medium. Ten minutes before the addition of chloramphenicol (50 µg/ml; t′ = 0), 1 mM IPTG was added to induce vapB. Samples were taken at the time points indicated and VapB detected by polyclonal antibodies directed towards VapB.