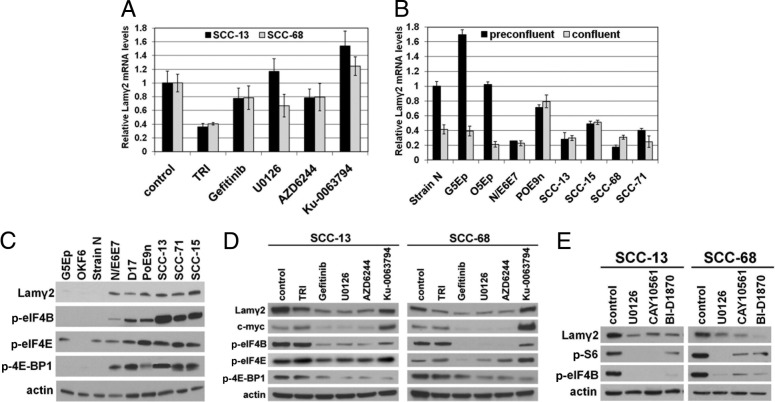
Figure 5.
Lamγ2 overexpression by neoplastic cells is unrelated to Lamγ2 mRNA levels, but correlates with ERK-dependent activation of translation initiation factors. A: Effects of kinase inhibitors on Lamγ2 mRNA levels in SCC cells. Confluent cultures were treated for 2 days with the inhibitors TRI, gefitinib, U0126, AZD6244, and Ku-0063794 and then were analyzed by qPCR for Lamγ2 mRNA, with results for each cell line internally normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels. Note the decrease in Lamγ2 mRNA levels resulting from treatment with TRI, but not with the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib or the MEK inhibitors U0126 and AZD6244, which block Lamγ2 protein synthesis in confluent SCC cultures. B: qPCR comparison of Lamγ2 mRNA levels in preconfluent and confluent cultures of normal and premalignant keratinocytes and SCC cells. Results shown are relative to Lamγ2 mRNA levels in preconfluent cultures of strain N keratinocytes, set at an arbitrary unit of 1. Note lower levels of Lamγ2 mRNA in neoplastic cells than in normal keratinocytes and absence of cell density-dependent mRNA decreases in neoplastic cells, compared with normal keratinocytes. C: Western blot analysis of activated forms of translation initiation factors in normal and premalignant keratinocytes and SCC cells. Note increased levels of p-eIF4B, p-eIF4E, and p-4E-BP1 in premalignant keratinocytes and SCC cells, compared with normal keratinocytes. D: Western blot analysis of effects of 2-day treatment of confluent SCC cultures with kinase inhibitors on levels of Lamγ2, c-myc, and phosphorylated states of translation initiation factors. Note strong reduction of Lamγ2, c-myc, and p-eIF4B levels in response to the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib and the MEK inhibitors U0126 and AZD6244, in contrast to small or no effect of the TORC1/2 inhibitor Ku-0063794. E: Western blot analysis of the effects on levels of Lamγ2 and p-eIF4B of 2-day treatments of confluent SCC cultures with ERK and RSK inhibitors, compared with U0126 treatment. Note that ERK and RSK inhibitors substantially reduced Lamγ2 and p-eIF4B levels.