Figure 2.
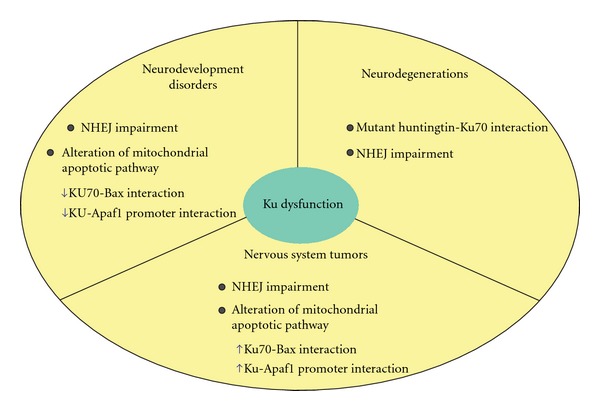
Ku dysfunction can lead to pathological states of the nervous system. Besides NHEJ impairment, which results in DNA damage accumulation, Ku-related alterations of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway can play a crucial role in neurodevelopment disorders and neoplastic transformations. In particular, Bax-Ku70 and/or Apaf1 promoter-Ku interaction can be decreased and lead to massive apoptosis upon Ku loss of function, as observable in Ku-related disorders of neurodevelopment. Alternatively, Ku gain of function in tumors of the nervous system may lead to an increase of Ku binding to Bax and/or the Apaf1 promoter, thus leading to evade apoptosis and to increase chemoresistance. On the other hand, in a mature nervous system, Ku sequestration mediated by mutant huntingtin can contribute to the HD pathology, by leading to an altered DSBs repair by NHEJ.
