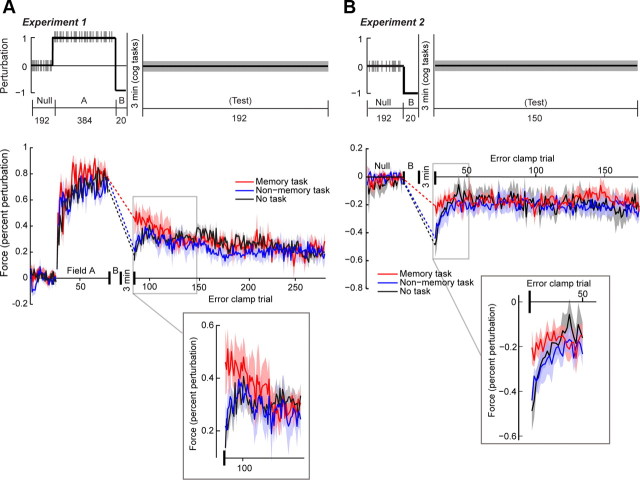
Figure 2.
A, Experiment 1 experiment design (top) and performance (bottom). Participants train in a null block (no perturbation), followed by field A (positive perturbation), field B (negative perturbation), and a test block (100% error-clamp trials). Inset shows the initial trials of the test block. The “nonmemory task” and “no task” groups exhibit spontaneous recovery, but the “memory task” group does not. B, Experiment 2 design (top) and performance (bottom). Participants train in a null block (no perturbation), followed by field B (negative perturbation) and a test block (100% error-clamp trials). The memory task disrupts the memory of field B. Vertical tick marks indicate error-clamp trials in the experiment design subfigure. Shaded regions of the data indicate SEM.