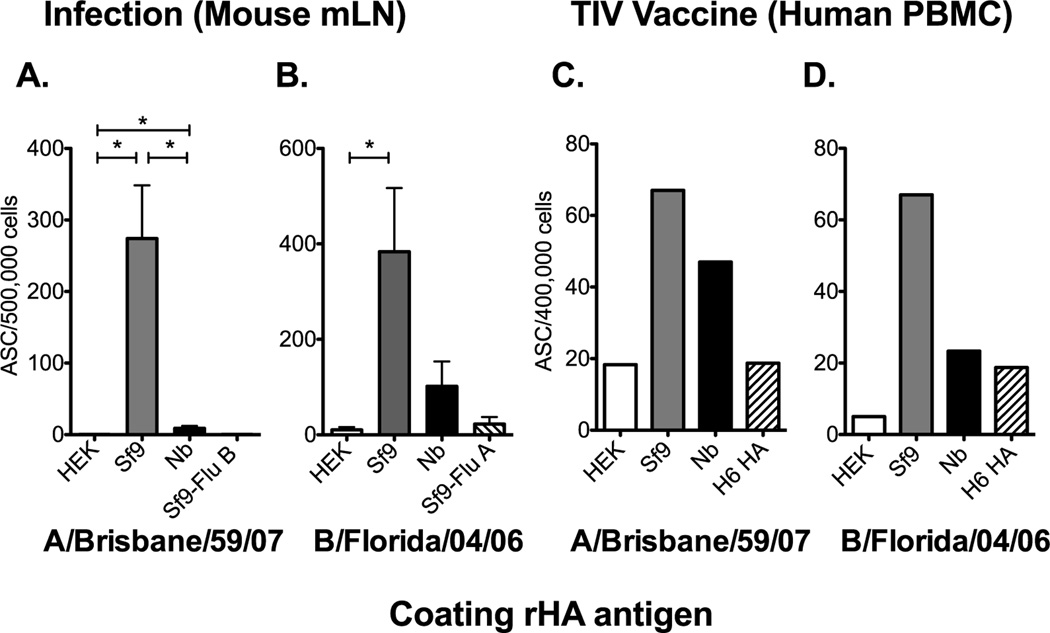
Figure 4. The rHA production process significantly affects its antigenicity in a B cell ELISPOT assay.
(A) B6 female mice were infected intranasally with 150,000 EID50 of A/Brisbane/59/07 and the mLN was harvested 12 days post infection. Mediastinal LNs from 12 mice were pooled in groups of 2 and processed into single cell suspensions. (B) B6 mice were infected with 6000 EID50 of B/Florida/04/06 and the mLN were harvested at day 12 days post infection. Single cell suspensions from individual mice were added into the plate. Mean ASC frequencies and standard error of the mean are presented in panel A and B. PBMCs, collected 7 days post seasonal influenza vaccination, from one vaccinated human subject were plated (4×105 cells/well) and diluted two-fold down the plate. HA-specific IgG secreting cells against the rHA from A/Brisbane/59/07 or B/Florida/04/06 are presented in C and D respectively. Mean ASC frequencies are plotted in C and D. Error bars represent the standard deviation between normalized wells. For panel A and B, Mann-Whitney (t-test) statistical analysis was performed with n = 5–6 and * = p<0.002.