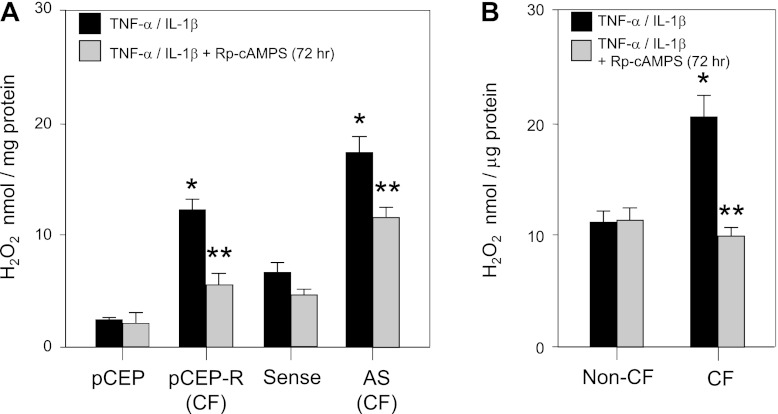
Fig. 2.
Rp-cAMPS modulates H2O2 levels in CF airway epithelia. H2O2 plays a key role the propagation of inflammatory signaling following stimulation with TNF-α and IL-1β. To examine the normalization of H2O2 levels following stimulation, Amplex red was used to measure whole cell H2O2 24 h poststimulation. Matched cell line pairs were grown to confluence and then maintained in the absence (solid bars) or presence (shaded bars) of 50 μM Rp-cAMPS for 72 h. Cells were then stimulated with TNF-α/IL-1β (10 ng/ml each) overnight and lysed, and intracellular levels of H2O2 were analyzed. A: intracellular H2O2 levels in CF cell line model pairs. B: intracellular H2O2 levels in non-CF and CF primary airway epithelia grown at an air-liquid interface. *Significant difference (P < 0.05) from non-CF control. **Significant difference (P < 0.05) from untreated CF cells. Error bars represent SE.