Fig. 1.
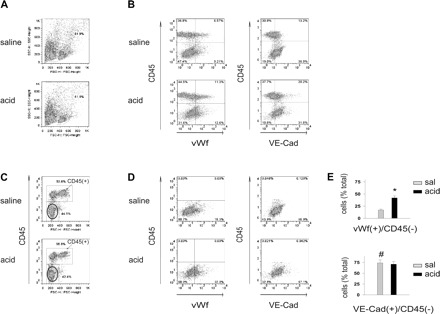
Airway acid increases the vWf+ fraction of cells isolated from the pulmonary vasculature. vWf, von Willebrand factor; VE-Cad, VE-cadherin. Pulmonary vascular cells were freshly isolated from mice subjected to intranasal saline or acid instillation. Dot plots from single experiments show expressions (% of total). The x and y ordinates (gray lines) indicate nonimmune isotype-specific IgG label. A: forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) on isolated cells. Particles and granular clumps are outside the boundary line. B: plots show cells labeled on CD45 and vWf (left) and CD45 and VE-cadherin (right). C: CD45− fraction (encircled). D: plots show vWf+ (left) and VE-cadherin+ (right) cells in CD45− fraction. E: group data of vWf+ and VE-cadherin+ cells in CD45− fractions, respectively, n = 4 mice each bar. Means ± SE, *P < 0.05 compared with bar on left, #P < 0.05 comparing saline (sal) instillation data for VE-cadherin and vWf.
