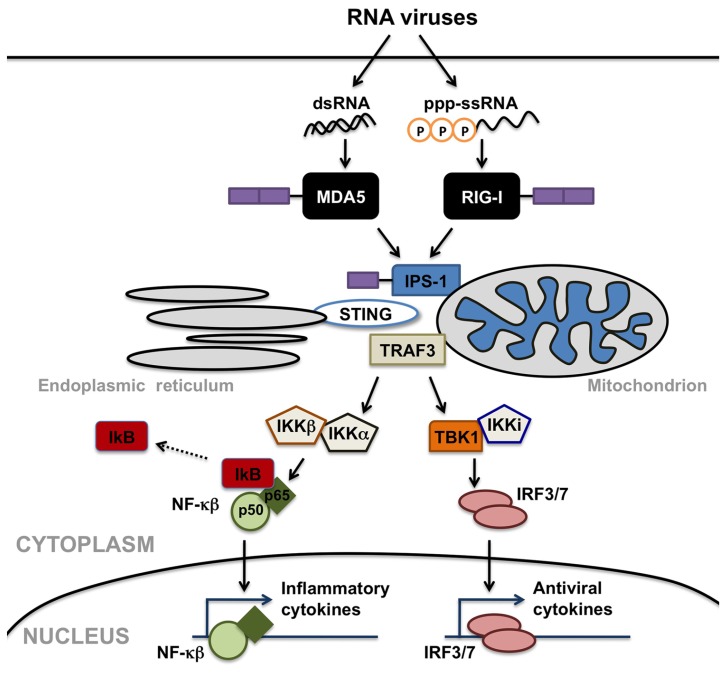
FIGURE 1.
Retinoic acid inducible gene (RIG)-I-like receptors serve as cytosolic sensors for viral RNA motifs and can initiate anti-viral and inflammatory cell responses. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) recognizes double-stranded RNA moieties (dsRNA), while RIG-I perceives short single or double-stranded RNAs with 5’ triphosphate ends (ppp-ssRNA). Helicase interaction with these viral RNAs induces the recruitment of downstream effector molecules including mitochondrial- or peroxisomal-associated interferon promoter stimulator (IPS)-1, TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) 3, and/or stimulator of interferon genes (STING), leading to the activation of IκB kinase (IKK)-related kinases, TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator binding kinase 1 (TBK1), and IKK-I. These kinases activate the transcription factors NF-κB and interferon-regulatory factors (IRF) 3, which translocate into the nucleus and activate transcription of anti-viral and inflammatory cytokines.