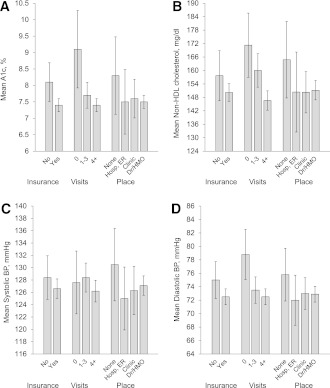
Figure 1.
Multivariate-adjusted predicted means (95% CI) of diabetes control indicators associated with health care access in U.S. adults with diabetes aged 18–64 years. A: y-axis, mean A1C (%); x-axis, access to care. B: y-axis, mean non-HDL cholesterol (mg/dL); x-axis, access to care. C: y-axis, mean systolic blood pressure (BP) (mmHg); x-axis, access to care. D: y-axis, mean diastolic blood pressure (mmHg); x-axis, access to care. Predicted means calculated from separate linear regression models of A1C (A), non-HDL cholesterol (B), systolic blood pressure (C), and diastolic blood pressure (D) associated with health care access indicators, adjusting for age, sex, race, marital status, education, family PIR, BMI, smoking status, family history of diabetes, diabetes medication use, and self-reported health. Analysis of A1C was restricted to NHANES 1999–2006. Clin, clinics; Dr, doctor; Hosp ER, hospital emergency room.