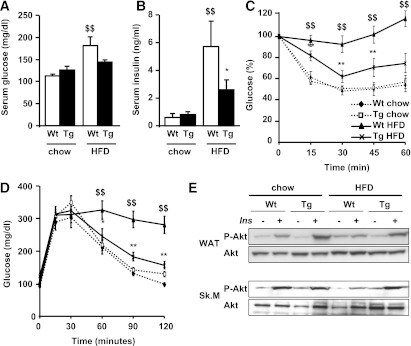
FIG. 6.
aP2VEGF transgenic (Tg) mice are protected against diet-induced glucose intolerance and insulin resistance compared with wild-type (Wt) mice. Blood glucose (A) and insulin (B) levels are shown in chow and HFD-fed mice. Data represent the mean ± SEM of at least 10 animals per group. C: Insulin sensitivity was determined after an intraperitoneal injection of insulin (0.75 units/kg body weight). Results are calculated as the percentage of initial blood glucose levels. Data represent the mean ± SEM of at least eight animals per group. D: Glucose tolerance was determined in fasted mice after an intraperitoneal injection of glucose (2 g/kg body weight), and blood glucose levels were measured at the indicated time points. Data represent the mean ± SEM of at least eight animals per group. E: Representative Western blots are shown for total Akt and phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) levels in WAT and skeletal muscle (Sk.M) before and after insulin stimulation in chow- and HFD-fed mice, as indicated in research design and methods. *P < 0.05 vs. Wt HFD. **P < 0.01 vs. Wt HFD. $$P < 0.01 vs. Wt chow.