Figure 7. Peripheral versus central antagonism of the effects of systemic CCK8 on DMN spontaneous activity.
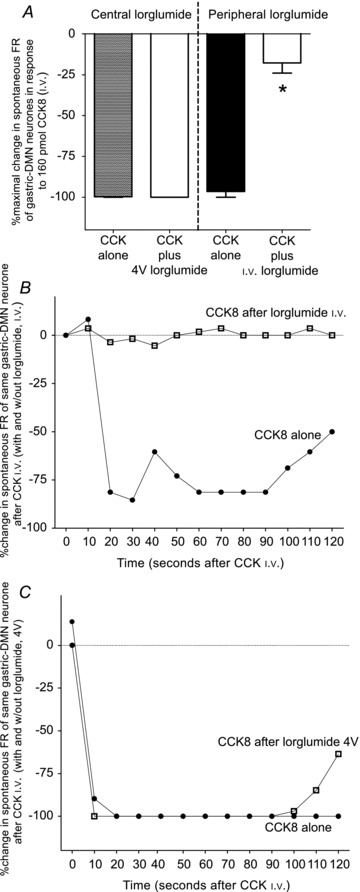
A, bar graph represents averaged maximal effects of CCK8 to inhibit spontaneous DMN firing rate with and without lorglumide administered either centrally or peripherally. Application of lorglumide to the 4V floor has no effect on the attenuation of the spontaneous activity of the gastric-DMN neurones evoked by systemic CCK8 in fasted rats. In contrast, i.v.-administered lorglumide reduced the attenuating effect of CCK8 on the spontaneous activity of the gastric-DMN neurones by approximately 80% (F3,16= 112; P < 0.0001). B, plot of the spontaneous activity of an identified gastric-DMN neurone exposed to CCK8 with and without i.v.-administered lorglumide. Note that the CCK8 effect is completely blocked after i.v. lorglumide. C, similar plot of the spontaneous activity of an identified gastric-DMN neurone exposed to CCK8 with and without 4V-administered lorglumide. Spontaneous activity of this gastric-DMN neurone was not affected following 4V application of lorglumide.
