Figure 7.
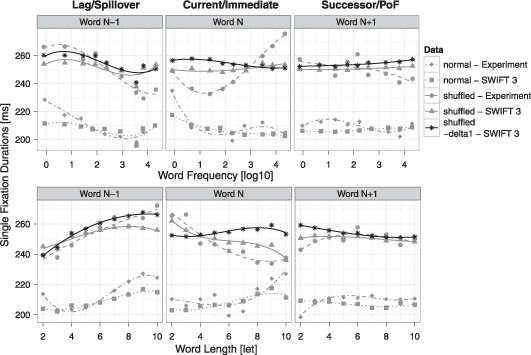
Effects of the dynamical processing span on spatially distributed word processing. Shown are the same results as in Figure 4 (grey), including model simulations of shuffled (triangles & solid lines) and of normal (squares & dotted lines) text and experimental data on shuffled (points & dashed lines) and normal (diamonds & dot-dashed lines) text reading. In addition, simulations of the shuffled-SWIFT model are presented, where the strong dynamic modulation of the processing span was disabled (black stars & solid lines, “shuffled – delta1”). Top row: Average single fixation durations as a function of word frequency of the previous word (word N–1, left column), the current word (word N, middle column), and the next word (word N+1, right column). Predictions from separate regression analyses involving cubic effects on averaged data for each condition are shown. Bottom row: Corresponding plots as a function of word length.
