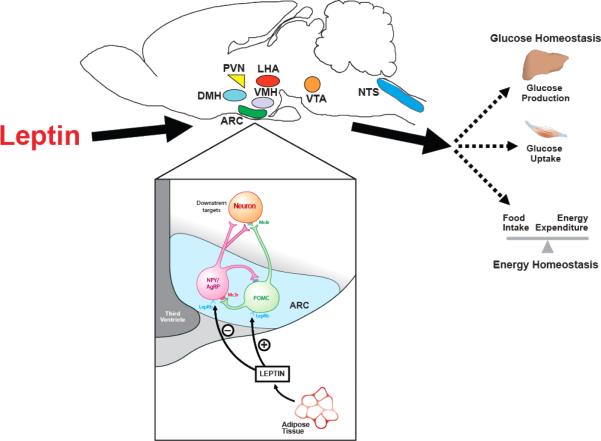
FIGURE 4. CNS neurocircuits regulating energy and glucose homeostasis.
A number of hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic sites have been implicated in the action of leptin to regulate energy and glucose homeostasis. The hypothalamic ARC contains neuropeptide Y and agouti-related peptide (NPY/AgRP) neurons that stimulate food intake and are inhibited by leptin, and pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons that reduce food intake and are stimulated by leptin. NPY/AgRP neurons also inhibit POMC neurons via synaptic release of the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). ARC, arcuate nucleus; LepRb, leptin receptor; Mc3r/Mc4r, melanocortin-3/4 receptor; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; DMH, dorsomedial hypothalamus; VTA, ventral tegmental area; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract.