Figure 2.
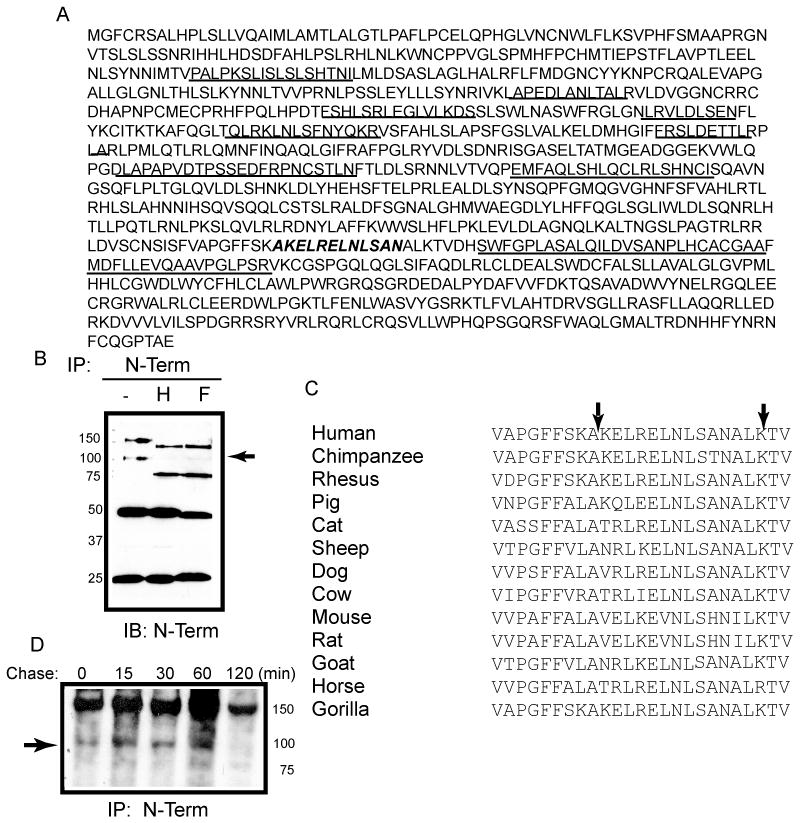
Identification of the C-terminal boundary of sTLR9 by tandem mass spectrometry. (A) Human TLR9 ecto-domain amino acid sequence with the peptides that were identified and sequenced by tandem mass spectrometry underlined and the predicted cleavage site italicized and bolded. (B) HEK 293 cells expressing TLR9-YFP were immunoprecipitated with anti-TLR9 and were either untreated (−) or treated with either endo H (H), or PNGase F (F) prior to resolving by SDS-PAGE and assaying by immunoblotting for the N-terminus (anti-TLR9). ➛ deglycosylated soluble TLR9 (C) Alignment of TLR9 LRRs 24–25 from different species. Arrows indicate the boundaries of the identified proteolytic site. (D) Pulse-chase analysis of proteolytic generation of sTLR9 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. ➛ sTLR9. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
