Figure 3.
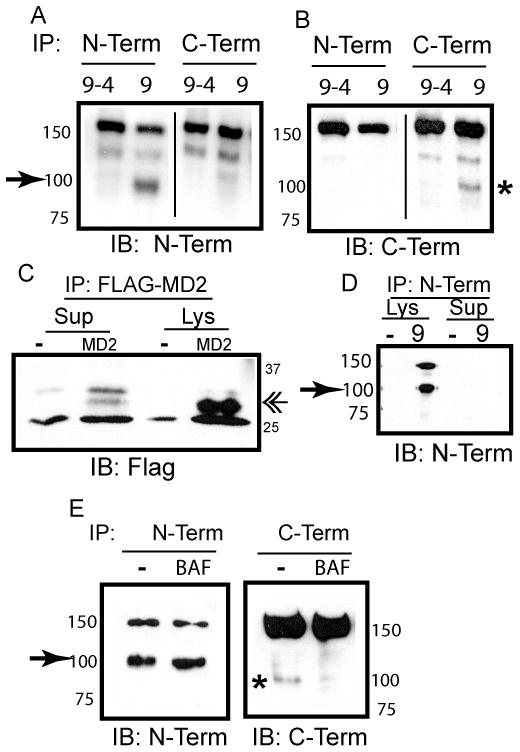
sTLR9 is generated and retained in endosomes, but independently of acidic proteases. (A) HEK 293 cells expressing TLR9–4-GFP (9–4) or TLR9-YFP (9) were immunoprecipitated for TLR9 (N-Term) or GFP/YFP (C-Term). Following resolution by SDS-PAGE and transfer to nitrocellulose, immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for TLR9 (N-Term).➛ sTLR9 (B) As in (A), except that membranes were immunoblotted for GFP/YFP (C-Term). * p80 (C) Lysates (Lys) or cell culture supernatants (Sup) from HEK 293 cells (−) or HEK 293 cells expressing Flag-MD2 (MD2) were immunoprecipitated, and assayed by immunoblotting for Flag. «-MD2 (D) Lysates (Lys) or cell culture supernatants (Sup) from HEK 293 cells (−) or HEK 293 cells expressing TLR9-YFP (9) were immunoprecipitated for TLR9 (N-Term), and assayed by immunoblotting for TLR9 (N-Term). ➛ sTLR9 (E) HEK 293 cells stably expressing TLR9-YFP were treated with DMSO (−) or 100 nM Bafilomycin A1 (BAF) for 7 hours at 37°C. Lysates were immunoprecipitated for TLR9 (N-Term) or GFP/YFP (C-Term), and assayed by immunoblotting for TLR9 (N-Term) or GFP/YFP (C-Term). ➛ sTLR9; * p80. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
