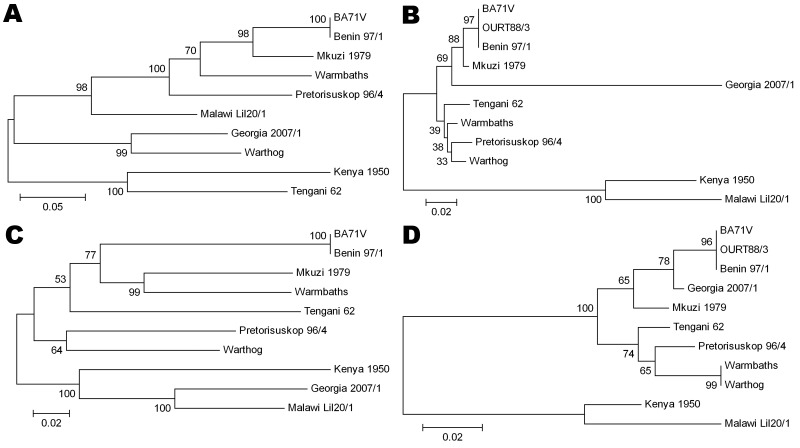
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic trees of 4 of the most divergent African swine fever virus proteins. A) C-type lectin EP153R, B) A238L, C) CD2-like protein EP402R, D) structural protein K177R (P22). Evolutionary history was inferred by using the neighbor-joining method. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 1,000 replicates is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the proteins analyzed. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in <50% bootstrap replicates are collapsed. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated proteins clustered in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated from the dataset (complete deletion option). There were 224 positions in the final dataset. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted in MEGA4 (27). Scale bars indicate amino acid substitutions per site.