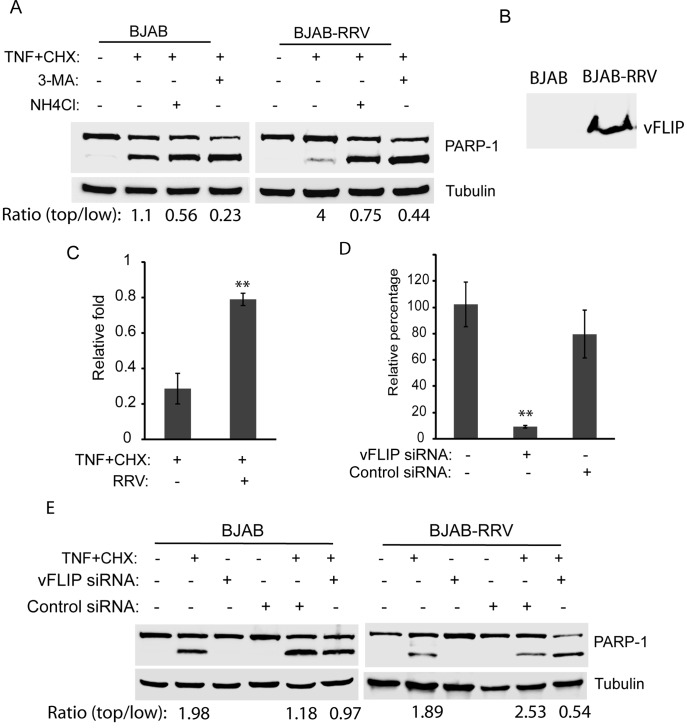
Figure 5. RRV latent infection of BJAB cells protects the cells from apoptosis.
A. RRV latent infection of BJAB cells protects the cells against apoptosis and inhibition of autophagy abolishes the protective effect. BJAB cells latently infected with RRV (BJAB-RRV) were either untreated, treated with 3-MA for 3 h prior apoptosis induction by TNF-α and cycloheximide, or treated with ammonium chloride at the same time of the apoptosis induction. The cells were harvested 2 h post-apoptosis induction for Western blotting of PARP-1 cleavage. Similar treatment of uninfected BJAB cells was included as a control. The ratio of top PARP-1 band to low band is shown under the image. B. Detection of vFLIP in RRV-infected BJAB cells by Western blotting with rabbit anti-vFLIP antibody. C. Cell viability assay of BJAB and BJAB-RRV cells 3 h after apoptosis induction. Relative folds in comparison with uninfected BJAB cells at 0 h are shown. Significant differences between BJAB and BJAB-RRV cells after apoptosis induction are denoted by “**", which indicates P<0.01. D. Suppression vFLIP expression in RRV-infected BJAB cells by siRNA. BJAB cells latently infected with RRV were transfected with a siRNA against vFLIP. An irrelevant siRNA was included as a control. Real-time RT-PCR was conducted to assess vFLIP transcript level. Relative percentages in comparison with mock-treated control are shown. Significant differences between siRNA-treated and mock-treated BJAB-RRV cells are denoted by “**". E. Suppression of RRV vFLIP gene expression in BJAB-RRV cells leads to loss of the capability against apoptosis. BJAB cells latently infected with RRV were transfected with siRNA against vFLIP 15 h before apoptosis induction. Treatment of uninfected BJAB cells was included as a control. The cells were harvested 2 h after treatment with TNF-α and cycloheximide for Western blotting of PARP-1 cleavage. The ratios of top PARP-1 band to low band are shown under the image.