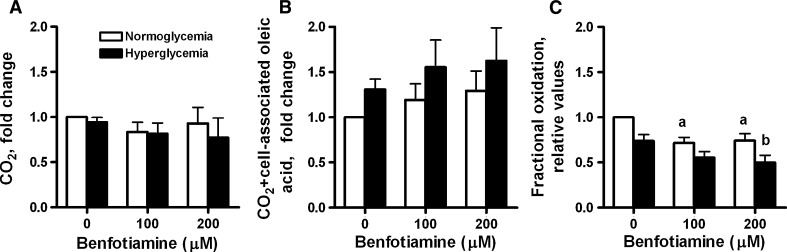
Fig. 4.
The effects of benfotiamine on a [1-14C]oleic acid (OA) oxidation, b overall OA utilization (sum of CO2 formation and cell-associated OA) and c fractional oxidation of OA (CO2/(sum of cell-associated plus CO2)) of OA under NG (5.5 mM glucose) and HG (20 mM glucose) conditions. Myotubes were treated for 4 days with or without benfotiamine (100 and 200 μM) under NG and HG conditions. All data are normalized to normoglycemic control cells and presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5 for NG and n = 6 for HG, independent muscle cell donors). aP < 0.05 versus control myotubes not exposed to benfotiamine under NG conditions; bP < 0.05 versus control myotubes not exposed to benfotiamine under HG conditions (LMM). HG treatment significantly decreased fractional oleic acid oxidation (P < 0.01 overall effect) (LMM)