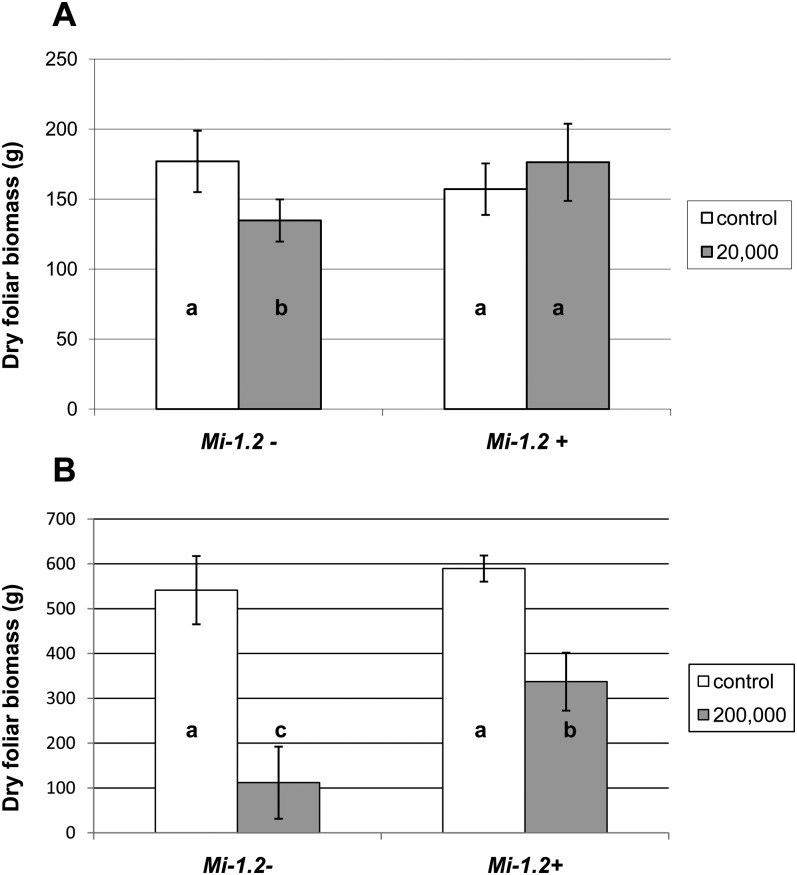
Fig. 1.
Effects of Mi-mediated resistance and nematode inoculation on dry foliar weight (±S.D.) of tomato plants. Plants were inoculated with 20,000 (A) and 200,000 (B) nematode eggs, while control plants were mock-inoculated with water. Foliar dry weight was analyzed by Two-way ANOVA. Where there was a significant interaction between treatment and genotype, mean separations were also performed using Student’s t-tests (values followed by the same letter are not significantly different from each other at α=0.05). (A) When plants were inoculated with 20,000 nematode eggs, nematode inoculation significantly reduced foliar dry weight of the susceptible (Mi-1.2-) genotype, but not the resistant (Mi-1.2+) cultivar. (B) At the higher inoculum level, both genotypes suffered a reduction in foliar biomass, but this reduction was significantly greater in the susceptible cultivar. Seven of eight susceptible plants inoculated with nematodes were harvested about 3 months earlier than other plants because they were succumbing to nematode infection.