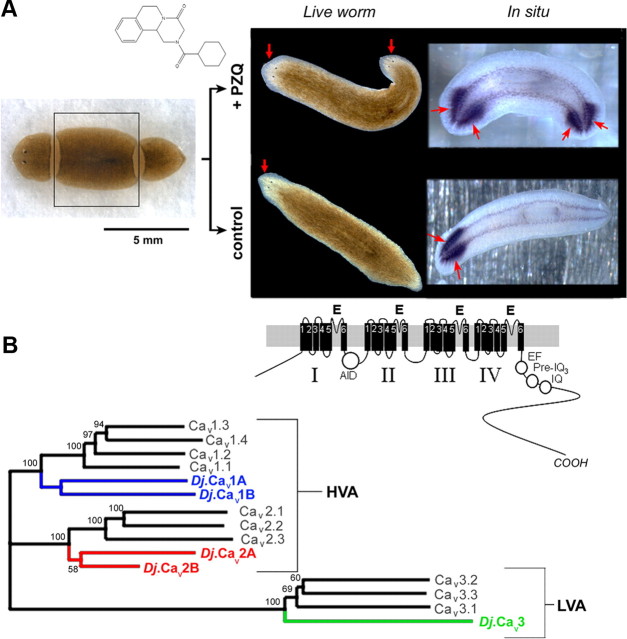
Figure 1.
PZQ-evoked bipolarity and characterization of planarian Cavα subunits. A, Left, Overview of regenerative assay. Trunk fragment (boxed) was isolated and incubated with PZQ (structure, top) in samples to be compared with control worms (bottom). Right, Images of bipolar worms (head, arrowed) produced after PZQ exposure (top) in live worms (left) and samples stained for the CNS marker PC2 (right). Control worms are shown for comparison (bottom). B, Phylogenetic analysis of sequence homology between planarian and human Cavα sequences aligned using MUSCLE and displayed as an unrooted tree assembled by a neighbor joining algorithm (Geneious 5.0). Bootstrap values are indicated at nodes. The lower value for D. japonica Cav2 subunits relates to the use of partial sequences. Accession numbers are referenced in Table 1, with addition of Cav2.1 (O00555), Cav2.2 (Q00975), Cav3.2 (O95180), and Cav3.3 (Q9P0X4). The D. japonica subunit previously referred to as Cav1.1 (Nogi et al., 2009) is renamed Cav2A to standardize nomenclature with the Schistosome literature (Kohn et al., 2001b). Inset, Schematic of Cav1 architecture (domains I–IV) and motifs (α-interaction domain, AID; EF-hand motif, EF; pre-IQ3 and IQ motif).